PPM1G and its diagnostic, prognostic and therapeutic potential in HCC (Review)
- PMID: 39329206
- PMCID: PMC11436262
- DOI: 10.3892/ijo.2024.5697
PPM1G and its diagnostic, prognostic and therapeutic potential in HCC (Review)
Abstract
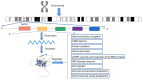
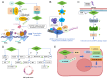
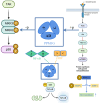
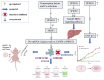
Global statistics indicate that hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is the sixth most common cancer and the third leading cause of cancer‑related death. Protein phosphatase Mg2+/Mn2+ dependent 1G (PPM1G, also termed PP2Cγ) is one of the 17 members of the PPM family. The enzymatic activity of PPM1G is highly reliant on Mg2+ or Mn2+ and serves as a dephosphorylation regulator for numerous key proteins. PPM1G, functioning as a phosphatase, is involved in a number of significant biological processes such as the regulation of eukaryotic gene expression, DNA damage response, cell cycle and apoptosis, cell migration ability, cell survival and embryonic nervous system development. Additionally, PPM1G serves a role in regulating various signaling pathways. In recent years, further research has increasingly highlighted PPM1G as an oncogene in HCC. A high expression level of PPM1G is closely associated with the occurrence, progression and poor prognosis of HCC, offering notable diagnostic and therapeutic value for this patient population. In the present review, the regulatory role of PPM1G in diverse biological processes and signaling pathway activation in eukaryotes is evaluated. Furthermore, its potential application as a biomarker in the diagnosis and prognosis evaluation of HCC is assessed, and future prospects for HCC treatment strategies centered on PPM1G are discussed.
Keywords: biomarkers; diagnosis; hepatocellular carcinoma; liver fibrosis; prognosis; protein phosphatase Mg2+/Mn2+ dependent 1G; therapeutic.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declared that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
High expression of PPM1G is associated with the progression and poor prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma.Cancer Biomark. 2022;34(1):13-22. doi: 10.3233/CBM-203248. Cancer Biomark. 2022. PMID: 34366322
-
PPM1G promotes the progression of hepatocellular carcinoma via phosphorylation regulation of alternative splicing protein SRSF3.Cell Death Dis. 2021 Jul 21;12(8):722. doi: 10.1038/s41419-021-04013-y. Cell Death Dis. 2021. PMID: 34290239 Free PMC article.
-
PPM1G-mediated TBL1X mRNA splicing promotes cell migration in hepatocellular carcinoma.Cancer Sci. 2025 Jan;116(1):67-80. doi: 10.1111/cas.16372. Epub 2024 Oct 27. Cancer Sci. 2025. PMID: 39462759 Free PMC article.
-
The role of micro-RNAs in hepatocellular carcinoma: from molecular biology to treatment.Molecules. 2014 May 19;19(5):6393-406. doi: 10.3390/molecules19056393. Molecules. 2014. PMID: 24853455 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Hippo pathway in hepatocellular carcinoma: Non-coding RNAs in action.Cancer Lett. 2017 Aug 1;400:175-182. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2017.04.032. Epub 2017 Apr 29. Cancer Lett. 2017. PMID: 28461246 Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

