AUP1 transcriptionally activated by KDM5B reprograms lipid metabolism to promote the malignant progression of cervical cancer
- PMID: 39329209
- PMCID: PMC11436259
- DOI: 10.3892/ijo.2024.5695
AUP1 transcriptionally activated by KDM5B reprograms lipid metabolism to promote the malignant progression of cervical cancer
Abstract
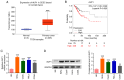
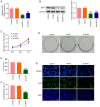
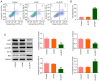
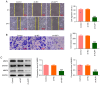
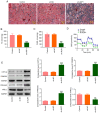
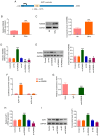
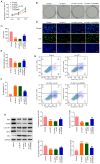
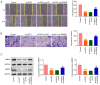
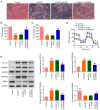
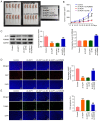
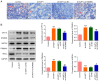
Cervical cancer is one of the reproductive malignancies threatening women's lives worldwide. In the present study, it was aimed to explore the role and mechanism of ancient ubiquitous protein 1 (AUP1) in cervical cancer. Through bioinformatics analysis, AUP1 expression in cervical cancer tissues and the correlation between AUP1 and the prognosis of patients were analyzed. AUP1 expression in several cervical cancer cell lines was detected. Following the co‑transfection of short hairpin RNA specific to AUP1 with or without lysine demethylase 5B (KDM5B) overexpression plasmids in SiHa cells, the proliferation and apoptosis of SiHa cells were detected. Additionally, wound healing and Transwell assays were used to detect SiHa cell migration and invasion. Cellular lipid droplets level was detected using the Oil red O staining. Meantime, the levels of triglyceride, cholesterol, oxygen consumption rates and expression of lipid metabolism‑related proteins were detected to assess the lipid metabolism in SiHa cells. Then, the luciferase reporter assay and ChIP assay were used to verify the binding between KDM5B and AUP1. Finally, the effects of AUP1 and KDM5B on the growth and lipid metabolism in SiHa tumor‑bearing mice were measured. AUP1 was significantly upregulated in cervical cancer tissues and cells. AUP1 interference inhibited the malignant biological behaviors and lipid metabolism reprogramming of SiHa cells, which was blocked by KDM5B overexpression. Moreover, KDM5B could transcriptionally activate AUP1 and upregulate AUP1 expression. Furthermore, AUP1 knockdown transcriptionally regulated by KDM5B limited the tumor growth and suppressed the lipid metabolism reprogramming in vivo. Collectively, AUP1 could be transcriptionally activated by KDM5B to reprogram lipid metabolism, thereby promoting the progression of cervical cancer. These findings reveal possible therapeutic strategies in targeting metabolic pathways.
Keywords: ancient ubiquitous protein 1; cervical cancer; lipid metabolism reprogramming; lysine demethylase 5B; proliferation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
LncRNA HOXC-AS3 accelerates malignant proliferation of cervical cancer cells via stabilizing KDM5B.J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2024 Jun 6;150(6):294. doi: 10.1007/s00432-024-05799-y. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38842683 Free PMC article.
-
Lysine demethylase 5B suppresses CC chemokine ligand 14 to promote progression of colorectal cancer through the Wnt/β-catenin pathway.Life Sci. 2021 Jan 1;264:118726. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2020.118726. Epub 2020 Nov 5. Life Sci. 2021. PMID: 33160990
-
Original Research: miR-194 inhibits proliferation and invasion and promotes apoptosis by targeting KDM5B in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma cells.Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2017 Jan;242(1):45-52. doi: 10.1177/1535370216662712. Epub 2016 Aug 1. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2017. PMID: 27480251 Free PMC article.
-
Histone demethylase lysine demethylase 5B in development and cancer.Oncotarget. 2017 Jan 31;8(5):8980-8991. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.13858. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 27974677 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Drawing a line between histone demethylase KDM5A and KDM5B: their roles in development and tumorigenesis.Exp Mol Med. 2022 Dec;54(12):2107-2117. doi: 10.1038/s12276-022-00902-0. Epub 2022 Dec 12. Exp Mol Med. 2022. PMID: 36509829 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Deciphering the tumor immune microenvironment: single-cell and spatial transcriptomic insights into cervical cancer fibroblasts.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2025 Jul 5;44(1):194. doi: 10.1186/s13046-025-03432-5. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2025. PMID: 40616092 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Nakisige C, Trawin J, Mitchell-Foster S, Payne BA, Rawat A, Mithani N, Amuge C, Pedersen H, Orem J, Smith L, Ogilvie G. Integrated cervical cancer screening in Mayuge District Uganda (ASPIRE Mayuge): A pragmatic sequential cluster randomized trial protocol. BMC Public Health. 2020;20:142. doi: 10.1186/s12889-020-8216-9. - DOI - PMC - PubMed

