Development and Evaluation of Fucoidan-Loaded Electrospun Polyvinyl Alcohol/Levan Nanofibers for Wound Dressing Applications
- PMID: 39329530
- PMCID: PMC11428952
- DOI: 10.3390/biomimetics9090508
Development and Evaluation of Fucoidan-Loaded Electrospun Polyvinyl Alcohol/Levan Nanofibers for Wound Dressing Applications
Abstract
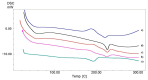
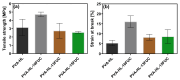
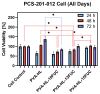
Wound dressing is an ancient technique for promoting healing, and modern technology has led to the development of advanced dressings that enhance patient care. Nanofiber-based wound dressings are a medical innovation with enhanced properties, including improved adhesion, reduced infection rates, and increased tissue regeneration. This article focuses on electrospun nanofibrous wound dressing materials produced using the widely adopted method of electrospinning. This article explores several parameters that influence fiber size, including electrical conductivity, electric potential, collector distance, viscosity, flow rate, and surface tension. With Fucoidan (FUC) loading, an increase in the fiber diameter of the control group from 310 nm to 395 nm was observed. This research also examines the use of Halomonas Levan (HL), a polysaccharide, and polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) polymer as wound dressing materials to enhance the mechanical properties of the latter. The incorporation of various concentrations of FUC into PVA-HL electrospun nanofibers yielded diverse effects on tensile strength: an enhancement was observed in the PVA-HL-10FUC formulation, while reductions were noted in the PVA-HL-13FUC and PVA-HL-15FUC formulations. The WST1 assay demonstrated that none of the samples exhibited cytotoxicity up to 72 h, as cell viability increased over time. In conclusion, nanofibrous PVA-HL structures loaded with FUC, which promote tissue regeneration and prevent infection, could be considered a novel wound dressing material.
Keywords: Halomonas Levan; electrospinning; fucoidan; polyvinyl alcohol; wound dressing.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Electrospun Chitosan-Polyvinyl Alcohol Nanofiber Dressings Loaded with Bioactive Ursolic Acid Promoting Diabetic Wound Healing.Nanomaterials (Basel). 2022 Aug 25;12(17):2933. doi: 10.3390/nano12172933. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36079971 Free PMC article.
-
Fucoidan-loaded electrospun Polyvinyl-alcohol/Chitosan nanofibers with enhanced antibacterial activity for skin tissue engineering.J Mech Behav Biomed Mater. 2023 Dec;148:106163. doi: 10.1016/j.jmbbm.2023.106163. Epub 2023 Oct 7. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater. 2023. PMID: 37832172
-
Co-electrospun nanofibrous mats loaded with bitter gourd (Momordica charantia) extract as the wound dressing materials: in vitro and in vivo study.BMC Complement Med Ther. 2021 Apr 7;21(1):111. doi: 10.1186/s12906-021-03284-4. BMC Complement Med Ther. 2021. PMID: 33827547 Free PMC article.
-
Production and Application of Biomaterials Based on Polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) as Wound Dressing.Chem Asian J. 2022 Nov 2;17(21):e202200595. doi: 10.1002/asia.202200595. Epub 2022 Sep 19. Chem Asian J. 2022. PMID: 36066570 Review.
-
An Overview on Application of Natural Substances Incorporated with Electrospun Nanofibrous Scaffolds to Development of Innovative Wound Dressings.Mini Rev Med Chem. 2018 Feb 14;18(5):414-427. doi: 10.2174/1389557517666170308112147. Mini Rev Med Chem. 2018. PMID: 28271816 Review.
Cited by
-
Investigation of Multifunctionality of Electrospun Poly(vinyl alcohol) Nanofiber Membranes Incorporating Boric Acid and Nanoencapsulated Curcumin: Filtration Performance, Antibacterial Activity, and Environmental Impact.ACS Omega. 2025 Jun 10;10(24):26106-26117. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.5c03317. eCollection 2025 Jun 24. ACS Omega. 2025. PMID: 40584345 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Borda L.J., Macquhae F.E., Kirsner R.S. Wound Dressings: A Comprehensive Review. Curr. Dermatol. Rep. 2016;5:287–297. doi: 10.1007/s13671-016-0162-5. - DOI
-
- Ambekar R.S., Kandasubramanian B. Advancements in Nanofibers for Wound Dressing: A Review. Eur. Polym. J. 2019;117:304–336. doi: 10.1016/j.eurpolymj.2019.05.020. - DOI
-
- Sandri G., Rossi S., Bonferoni M.C., Caramella C., Ferrari F. Therapeutic Dressings and Wound Healing Applications. Wiley Online Library; Hoboken, NJ, USA: 2020. Electrospinning Technologies in Wound Dressing Applications.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

