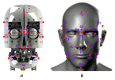
Advanced Design and Implementation of a Biomimetic Humanoid Robotic Head Based on Vietnamese Anthropometry
- PMID: 39329576
- PMCID: PMC11431037
- DOI: 10.3390/biomimetics9090554
Advanced Design and Implementation of a Biomimetic Humanoid Robotic Head Based on Vietnamese Anthropometry
Abstract
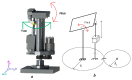
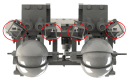
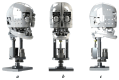
In today's society, robots are increasingly being developed and playing an important role in many fields of industry. Combined with advances in artificial intelligence, sensors, and design principles, these robots are becoming smarter, more flexible, and especially capable of interacting more naturally with humans. In that context, a comprehensive humanoid robot with human-like actions and emotions has been designed to move flexibly like a human, performing movements to simulate the movements of the human neck and head so that the robot can interact with the surrounding environment. The mechanical design of the emotional humanoid robot head focuses on the natural and flexible movement of human electric motors, including flexible suitable connections, precise motors, and feedback signals. The feedback control parts, such as the neck, eyes, eyebrows, and mouth, are especially combined with artificial skin to create a human-like appearance. This study aims to contribute to the field of biomimetic humanoid robotics by developing a comprehensive design for a humanoid robot head with human-like actions and emotions, as well as evaluating the effectiveness of the motor and feedback control system in simulating human behavior and emotional expression, thereby enhancing natural interaction between robots and humans. Experimental results from the survey showed that the behavioral simulation rate reached 94.72%, and the emotional expression rate was 91.50%.
Keywords: Vietnamese anthropometry; anatomy; emotional robot; geminoid robot; humanoid robot; robotics.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

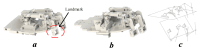




References
-
- Shishehgar M., Kerr D., Blake J. A systematic review of research into how robotic technology can help older people. Smart Health. 2018;7–8:1–18. doi: 10.1016/j.smhl.2018.03.002. - DOI
-
- Hentout A., Aouache M., Maoudj A., Akli I. Human–robot interaction in industrial collaborative robotics: A literature review of the decade 2008–2017. Adv. Robot. 2019;33:764–799. doi: 10.1080/01691864.2019.1636714. - DOI
-
- Burgoon J.K., Manusov V., Guerrero L.K. Nonverbal Communication. Routledge; London, UK: 2021.
-
- Kato I. Information-power machine with senses and limbs (Wabot 1); Proceedings of the First CISM-IFToMM Symposium on Theory and Practice of Robots and Manipulators; Udine, Italy. 5–8 September 1973; Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany: Springer; 1974. pp. 11–24.
-
- Breazeal C. Emotion and sociable humanoid robots. Int. J. Hum.-Comput. Stud. 2003;59:119–155. doi: 10.1016/S1071-5819(03)00018-1. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

