Artifact Management for Cerebral Near-Infrared Spectroscopy Signals: A Systematic Scoping Review
- PMID: 39329675
- PMCID: PMC11428271
- DOI: 10.3390/bioengineering11090933
Artifact Management for Cerebral Near-Infrared Spectroscopy Signals: A Systematic Scoping Review
Abstract
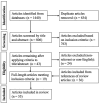
Artifacts induced during patient monitoring are a main limitation for near-infrared spectroscopy (NIRS) as a non-invasive method of cerebral hemodynamic monitoring. There currently does not exist a robust "gold-standard" method for artifact management for these signals. The objective of this review is to comprehensively examine the literature on existing artifact management methods for cerebral NIRS signals recorded in animals and humans. A search of five databases was conducted based on the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analysis guidelines. The search yielded 806 unique results. There were 19 articles from these results that were included in this review based on the inclusion/exclusion criteria. There were an additional 36 articles identified in the references of select articles that were also included. The methods outlined in these articles were grouped under two major categories: (1) motion and other disconnection artifact removal methods; (2) data quality improvement and physiological/other noise artifact filtering methods. These were sub-categorized by method type. It proved difficult to quantitatively compare the methods due to the heterogeneity of the effectiveness metrics and definitions of artifacts. The limitations evident in the existing literature justify the need for more comprehensive comparisons of artifact management. This review provides insights into the available methods for artifact management in cerebral NIRS and justification for a homogenous method to quantify the effectiveness of artifact management methods. This builds upon the work of two existing reviews that have been conducted on this topic; however, the scope is extended to all artifact types and all NIRS recording types. Future work by our lab in cerebral NIRS artifact management will lie in a layered artifact management method that will employ different techniques covered in this review (including dynamic thresholding, autoregressive-based methods, and wavelet-based methods) amongst others to remove varying artifact types.
Keywords: artifact management; bio signal analysis; cerebral hemodynamic monitoring; cerebral near-infrared spectroscopy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Artifact identification and removal methodologies for intracranial pressure signals: a systematic scoping review.Physiol Meas. 2024 Dec 17;45(12). doi: 10.1088/1361-6579/ad9af4. Physiol Meas. 2024. PMID: 39637554
-
Relationship Between Signals from Cerebral near Infrared Spectroscopy Sensor Technology and Objectively Measured Cerebral Blood Volume: A Systematic Scoping Review.Sensors (Basel). 2025 Feb 3;25(3):908. doi: 10.3390/s25030908. Sensors (Basel). 2025. PMID: 39943547 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of Morlet Wavelet Analysis for Artifact Detection in Low-Frequency Commercial Near-Infrared Spectroscopy Systems.Bioengineering (Basel). 2023 Dec 27;11(1):0. doi: 10.3390/bioengineering11010033. Bioengineering (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38247909 Free PMC article.
-
A systematic comparison of motion artifact correction techniques for functional near-infrared spectroscopy.Front Neurosci. 2012 Oct 11;6:147. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2012.00147. eCollection 2012. Front Neurosci. 2012. PMID: 23087603 Free PMC article.
-
The clinical effects of cerebral near-infrared spectroscopy monitoring (NIRS) versus no monitoring: a protocol for a systematic review with meta-analysis and trial sequential analysis.Syst Rev. 2021 Apr 16;10(1):111. doi: 10.1186/s13643-021-01660-2. Syst Rev. 2021. PMID: 33863369 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cope M. Ph.D. Thesis. University of London; London, UK: 1991. The Development of a near Infrared Spectroscopy System and Its Application for Non Invasive Monitoring of Cerebral Blood and Tissue Oxygenation in the Newborn Infants.
-
- Gomez A., Sainbhi A.S., Froese L., Batson C., Alizadeh A., Mendelson A.A., Zeiler F.A. Near Infrared Spectroscopy for High-Temporal Resolution Cerebral Physiome Characterization in TBI: A Narrative Review of Techniques, Applications, and Future Directions. Front. Pharmacol. 2021;12:719501. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.719501. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Brady K., Joshi B., Zweifel C., Smielewski P., Czosnyka M., Easley R.B., Hogue C.W. Real-Time Continuous Monitoring of Cerebral Blood Flow Autoregulation Using Near-Infrared Spectroscopy in Patients Undergoing Cardiopulmonary Bypass. Stroke. 2010;41:1951–1956. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.109.575159. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous