Ceramides-Emerging Biomarkers of Lipotoxicity in Obesity, Diabetes, Cardiovascular Diseases, and Inflammation
- PMID: 39329864
- PMCID: PMC11443555
- DOI: 10.3390/diseases12090195
Ceramides-Emerging Biomarkers of Lipotoxicity in Obesity, Diabetes, Cardiovascular Diseases, and Inflammation
Abstract
Abnormalities in lipid homeostasis have been associated with many human diseases, and the interrelation between lipotoxicity and cellular dysfunction has received significant attention in the past two decades. Ceramides (Cers) are bioactive lipid molecules that serve as precursors of all complex sphingolipids. Besides their function as structural components in cell and mitochondrial membranes, Cers play a significant role as key mediators in cell metabolism and are involved in numerous cellular processes, such as proliferation, differentiation, inflammation, and induction of apoptosis. The accumulation of various ceramides in tissues causes metabolic and cellular disturbances. Recent studies suggest that Cer lipotoxicity has an important role in obesity, metabolic syndrome, type 2 diabetes, atherosclerosis, and cardiovascular diseases (CVDs). In humans, elevated plasma ceramide levels are associated with insulin resistance and impaired cardiovascular and metabolic health. In this review, we summarize the role of ceramides as key mediators of lipotoxicity in obesity, diabetes, cardiovascular diseases, and inflammation and their potential as a promising diagnostic tool.
Keywords: cardiovascular diseases; ceramides; diabetes; inflammation; lipotoxicity.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
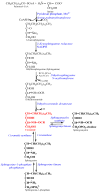
Figures

Similar articles
-
Sphingolipids as a Culprit of Mitochondrial Dysfunction in Insulin Resistance and Type 2 Diabetes.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021 Mar 18;12:635175. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2021.635175. eCollection 2021. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021. PMID: 33815291 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ceramides and Sphingosino-1-Phosphate in Obesity.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021 May 13;12:635995. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2021.635995. eCollection 2021. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021. PMID: 34054722 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ceramides - Lipotoxic Inducers of Metabolic Disorders.Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2015 Oct;26(10):538-550. doi: 10.1016/j.tem.2015.07.006. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2015. PMID: 26412155 Review.
-
Contribution of specific ceramides to obesity-associated metabolic diseases.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2022 Jul 5;79(8):395. doi: 10.1007/s00018-022-04401-3. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2022. PMID: 35789435 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Circulating Sphingolipids and Glucose Homeostasis: An Update.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Aug 12;24(16):12720. doi: 10.3390/ijms241612720. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37628901 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Post-translational modifications orchestrate mTOR-driven cell death in cardiovascular disease.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2025 Jul 15;12:1620669. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2025.1620669. eCollection 2025. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2025. PMID: 40734978 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Diabetic Ketoacidosis Is Associated with Lower Serum Sphingolipids but Higher β-Hydroxybutyrate and Lactate: A Pilot Study.Pathophysiology. 2025 Jun 26;32(3):29. doi: 10.3390/pathophysiology32030029. Pathophysiology. 2025. PMID: 40700071 Free PMC article.
-
Dairy Wastewaters to Promote Mixotrophic Metabolism in Limnospira (Spirulina) platensis: Effect on Biomass Composition, Phycocyanin Content, and Fatty Acid Methyl Ester Profile.Life (Basel). 2025 Jan 26;15(2):184. doi: 10.3390/life15020184. Life (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40003594 Free PMC article.
-
Ceramide signaling in immunity: a molecular perspective.Lipids Health Dis. 2025 Jul 1;24(1):225. doi: 10.1186/s12944-025-02642-2. Lipids Health Dis. 2025. PMID: 40597360 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Barranco-Altirriba M., Alonso N., Weber R.J.M., Lloyd G.R., Hernandez M., Yanes O., Capellades J., Jankevics A., Winder C., Falguera M., et al. Lipidome characterisation and sex-specific differences in type 1 and type 2 diabetes mellitus. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2024;23:109. doi: 10.1186/s12933-024-02202-5. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Lee Y., Hirose H., Ohneda M., Johnson J.H., McGarry J.D., Unger R.H. β-Cell Lipotoxicity in the Pathogenesis of Non-Insulin-Dependent Diabetes Mellitus of Obese Rats: Impairment in Adipocyte-β-Cell Relationships. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 1994;91:10878–10882. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.23.10878. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Angarita-Rodríguez A., Matiz-González J.M., Pinzón A., Aristizabal A.F., Ramírez D., Barreto G.E., González J. Enzymatic Metabolic Switches of Astrocyte Response to Lipotoxicity as Potential Therapeutic Targets for Nervous System Diseases. Pharmaceuticals. 2024;17:648. doi: 10.3390/ph17050648. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

