Tuberculosis Diagnosis: Current, Ongoing, and Future Approaches
- PMID: 39329871
- PMCID: PMC11430992
- DOI: 10.3390/diseases12090202
Tuberculosis Diagnosis: Current, Ongoing, and Future Approaches
Abstract
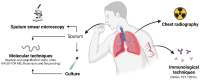
Tuberculosis (TB) remains an impactful infectious disease, leading to millions of deaths every year. Mycobacterium tuberculosis causes the formation of granulomas, which will determine, through the host-pathogen relationship, if the infection will remain latent or evolve into active disease. Early TB diagnosis is life-saving, especially among immunocompromised individuals, and leads to proper treatment, preventing transmission. This review addresses different approaches to diagnosing TB, from traditional methods such as sputum smear microscopy to more advanced molecular techniques. Integrating these techniques, such as polymerase chain reaction (PCR) and loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP), has significantly improved the sensitivity and specificity of M. tuberculosis identification. Additionally, exploring novel biomarkers and applying artificial intelligence in radiological imaging contribute to more accurate and rapid diagnosis. Furthermore, we discuss the challenges of existing diagnostic methods, including limitations in resource-limited settings and the emergence of drug-resistant strains. While the primary focus of this review is on TB diagnosis, we also briefly explore the challenges and strategies for diagnosing non-tuberculous mycobacteria (NTM). In conclusion, this review provides an overview of the current landscape of TB diagnostics, emphasizing the need for ongoing research and innovation. As the field evolves, it is crucial to ensure that these advancements are accessible and applicable in diverse healthcare settings to effectively combat tuberculosis worldwide.
Keywords: Mycobacterium tuberculosis; diagnostic techniques; molecular techniques; pulmonary tuberculosis diagnosis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures
References
-
- World Health Organization Global Tuberculosis Report 2023. 2023. [(accessed on 23 June 2024)]. Available online: https://www.who.int/teams/global-tuberculosis-programme/tb-reports/globa....
-
- Silva S., Arinaminpathy N., Atun R., Goosby E., Reid M. Economic impact of tuberculosis mortality in 120 countries and the cost of not achieving the Sustainable Development Goals tuberculosis targets: A full-income analysis. Lancet Glob. Health. 2021;9:e1372–e1379. doi: 10.1016/S2214-109X(21)00299-0. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

