A Theoretical Study of the Interaction of PARP-1 with Natural and Synthetic Inhibitors: Advances in the Therapy of Triple-Negative Breast Cancer
- PMID: 39329910
- PMCID: PMC11429593
- DOI: 10.3390/cimb46090558
A Theoretical Study of the Interaction of PARP-1 with Natural and Synthetic Inhibitors: Advances in the Therapy of Triple-Negative Breast Cancer
Abstract
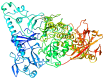
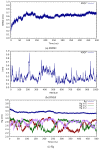
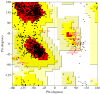
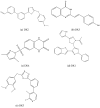
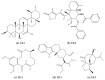
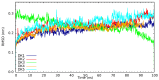
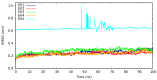
In the current study, we have investigated the secondary metabolites present in ethnomedical plants used for medicinal purposes-Astilbe chinensis (EK1), Scutellaria barbata D. Don (EK2), Uncaria rhynchophylla (EK3), Fallugia paradoxa (EK4), and Curcuma zedoaria (Christm.) Thread (EK5)-and we have compared them with five compounds of synthetic origin for the inhibition of PARP-1, which is linked to abnormal DNA replication, generating carcinogenic cells. We have studied these interactions through molecular dynamics simulations of each interacting system under physiological conditions (pH, temperature, and pressure) and determined that the compounds of natural origin have a capacity to inhibit PARP-1 (Poly(ADP-ribose) Polymerase 1) in all the cases inspected in this investigation. However, it is essential to mention that their interaction energy is relatively lower compared to that of compounds of synthetic origin. Given that binding energy is mandatory for the generation of a scale or classification of which is the best interacting agent, we can say that we assume that compounds of natural origin, having a complexation affinity with PARP-1, induce cell apoptosis, a potential route for the prevention of the proliferation of carcinogenic cells.
Keywords: PARP-1; docking; molecular dynamics simulation; molecular mechanics.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
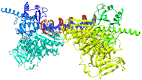


Similar articles
-
Identification of indole-based natural compounds as inhibitors of PARP-1 against triple-negative breast cancer: a computational study.J Biomol Struct Dyn. 2024 Mar;42(5):2667-2680. doi: 10.1080/07391102.2023.2208215. Epub 2023 May 8. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 2024. PMID: 37154583
-
In-silico method for elucidation of prodigiosin as PARP-1 inhibitor a prime target of Triple-negative breast cancer.Bioorg Chem. 2023 Sep;138:106618. doi: 10.1016/j.bioorg.2023.106618. Epub 2023 May 19. Bioorg Chem. 2023. PMID: 37244231
-
Virtual screening of small molecules databases for discovery of novel PARP-1 inhibitors: combination of in silico and in vitro studies.J Biomol Struct Dyn. 2017 Jul;35(9):1899-1915. doi: 10.1080/07391102.2016.1199328. Epub 2016 Jul 17. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 2017. PMID: 27315035
-
Poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase inhibitors in triple-negative breast cancer.Cancer J. 2010 Jan-Feb;16(1):48-52. doi: 10.1097/PPO.0b013e3181cf01eb. Cancer J. 2010. PMID: 20164690 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Natural inhibitors of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase-1.Mol Neurobiol. 2012 Aug;46(1):55-63. doi: 10.1007/s12035-012-8257-x. Epub 2012 Apr 4. Mol Neurobiol. 2012. PMID: 22476980 Review.
References
-
- Ramos Águila Y.d.l.C., Marimón Torres E.R., Crespo González C., Junco Sena B., Valiente Morejón W. Cáncer de mama, su caracterización epidemiológica. Rev. De Cienc. Médicas De Pinar Del Río. 2015;19:619–629.
-
- Vallejos-Sologuren C.S. Situación del Cáncer en el Perú. Diagnóstico. 2020;59:77–85. doi: 10.33734/diagnostico.v59i2.221. - DOI
-
- Quiñonero Muñoz F.J. Ph.D. Thesis. Universidad de Granada; Granada, Spain: 2023. Estudio de PARP-1 en Células Tumorales y Células Madre de Cáncer de Páncreas. Implicación en la Resistencia Tumoral y uso Como Diana Terapéutica.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

