Extracellular Vesicle-Derived Non-Coding RNAs: Key Mediators in Remodelling Heart Failure
- PMID: 39329911
- PMCID: PMC11430706
- DOI: 10.3390/cimb46090559
Extracellular Vesicle-Derived Non-Coding RNAs: Key Mediators in Remodelling Heart Failure
Abstract
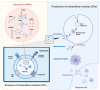
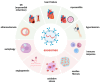
Heart failure (HF), a syndrome of persistent development of cardiac insufficiency due to various heart diseases, is a serious and lethal disease for which specific curative therapies are lacking and poses a severe burden on all aspects of global public health. Extracellular vesicles (EVs) are essential mediators of intercellular and interorgan communication, and are enclosed nanoscale vesicles carrying biomolecules such as RNA, DNA, and proteins. Recent studies have showed, among other things, that non-coding RNAs (ncRNAs), especially microRNAs (miRNAs), long ncRNAs (lncRNA), and circular RNAs (circRNAs) can be selectively sorted into EVs and modulate the pathophysiological processes of HF in recipient cells, acting on both healthy and diseased hearts, which makes them promising targets for the diagnosis and therapy of HF. This review aims to explore the mechanism of action of EV-ncRNAs in heart failure, with emphasis on the potential use of differentially expressed miRNAs and circRNAs as biomarkers of cardiovascular disease, and recent research advances in the diagnosis and treatment of heart failure. Finally, we focus on summarising the latest advances and challenges in engineering EVs for HF, providing novel concepts for the diagnosis and treatment of heart failure.
Keywords: biogenesis; engineered extracellular vesicles; exosome; extracellular vesicles; heart failure; microRNA; non-coding RNA.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Extracellular Non-Coding RNAs in Cardiovascular Diseases.Pharmaceutics. 2023 Jan 3;15(1):155. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15010155. Pharmaceutics. 2023. PMID: 36678784 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Extracellular Vesicles as Delivery Vehicles for Non-Coding RNAs: Potential Biomarkers for Chronic Liver Diseases.Biomolecules. 2024 Feb 26;14(3):277. doi: 10.3390/biom14030277. Biomolecules. 2024. PMID: 38540698 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Extracellular Vesicle MicroRNAs in Heart Failure: Pathophysiological Mediators and Therapeutic Targets.Cells. 2023 Aug 25;12(17):2145. doi: 10.3390/cells12172145. Cells. 2023. PMID: 37681877 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Plasma extracellular vesicle transcriptome as a dynamic liquid biopsy in acute heart failure.medRxiv [Preprint]. 2023 Feb 23:2023.02.17.23285936. doi: 10.1101/2023.02.17.23285936. medRxiv. 2023. PMID: 36865094 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
Emerging roles of extracellular vesicle-associated non-coding RNAs in hypoxia: Insights from cancer, myocardial infarction and ischemic stroke.Theranostics. 2022 Jul 18;12(13):5776-5802. doi: 10.7150/thno.73931. eCollection 2022. Theranostics. 2022. PMID: 35966580 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Exploring the landscape of exosomes in heart failure: a bibliometric analysis.Int J Surg. 2025 May 1;111(5):3356-3372. doi: 10.1097/JS9.0000000000002248. Int J Surg. 2025. PMID: 39869380 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Therapeutic potential of exosomal lncRNAs derived from stem cells in wound healing: focusing on mesenchymal stem cells.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2025 Feb 11;16(1):62. doi: 10.1186/s13287-025-04200-0. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2025. PMID: 39934913 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Davidson S.M., Padró T., Bollini S., Vilahur G., Duncker D.J., Evans P.C., Guzik T., Hoefer I.E., Waltenberger J., Wojta J., et al. Progress in cardiac research: From rebooting cardiac regeneration to a complete cell atlas of the heart. Cardiovasc. Res. 2021;117:2161–2174. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvab200. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Martin S.S., Aday A.W., Almarzooq Z.I., Anderson C.A.M., Arora P., Avery C.L., Baker-Smith C.M., Barone Gibbs B., Beaton A.Z., Boehme A.K., et al. 2024 Heart Disease and Stroke Statistics: A Report of US and Global Data from the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2024;149:e347–e913. doi: 10.1161/cir.0000000000001209. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Wang H., Li Y., Chai K., Long Z., Yang Z., Du M., Wang S., Zhan S., Liu Y., Wan Y., et al. Mortality in patients admitted to hospital with heart failure in China: A nationwide Cardiovascular Association Database-Heart Failure Centre Registry cohort study. Lancet Glob. Health. 2024;12:e611–e622. doi: 10.1016/S2214-109X(23)00605-8. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

