Brain Ischemic Tolerance Triggered by Preconditioning Involves Modulation of Tumor Necrosis Factor-α-Stimulated Gene 6 (TSG-6) in Mice Subjected to Transient Middle Cerebral Artery Occlusion
- PMID: 39329947
- PMCID: PMC11430743
- DOI: 10.3390/cimb46090595
Brain Ischemic Tolerance Triggered by Preconditioning Involves Modulation of Tumor Necrosis Factor-α-Stimulated Gene 6 (TSG-6) in Mice Subjected to Transient Middle Cerebral Artery Occlusion
Abstract
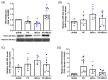
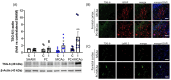
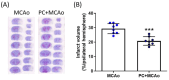
Ischemic preconditioning (PC) induced by a sub-lethal cerebral insult triggers brain tolerance against a subsequent severe injury through diverse mechanisms, including the modulation of the immune system. Tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α-stimulated gene 6 (TSG-6), a hyaluronate (HA)-binding protein, has recently been involved in the regulation of the neuroimmune response following ischemic stroke. Thus, we aimed at assessing whether the neuroprotective effects of ischemic PC involve the modulation of TSG-6 in a murine model of transient middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAo). The expression of TSG-6 was significantly elevated in the ischemic cortex of mice subjected to 1 h MCAo followed by 24 h reperfusion, while this effect was further potentiated (p < 0.05 vs. MCAo) by pre-exposure to ischemic PC (i.e., 15 min MCAo) 72 h before. By immunofluorescence analysis, we detected TSG-6 expression mainly in astrocytes and myeloid cells populating the lesioned cerebral cortex, with a more intense signal in tissue from mice pre-exposed to ischemic PC. By contrast, levels of TSG-6 were reduced after 24 h of reperfusion in plasma (p < 0.05 vs. SHAM), but were dramatically elevated when severe ischemia (1 h MCAo) was preceded by ischemic PC (p < 0.001 vs. MCAo) that also resulted in significant neuroprotection. In conclusion, our data demonstrate that neuroprotection exerted by ischemic PC is associated with the elevation of TSG-6 protein levels both in the brain and in plasma, further underscoring the beneficial effects of this endogenous modulator of the immune system.
Keywords: TSG-6; cerebral ischemia; neuroprotection; preconditioning; stroke.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Characterization of the Involvement of Tumour Necrosis Factor (TNF)-α-Stimulated Gene 6 (TSG-6) in Ischemic Brain Injury Caused by Middle Cerebral Artery Occlusion in Mouse.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Mar 18;24(6):5800. doi: 10.3390/ijms24065800. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36982872 Free PMC article.
-
Ischemic Preconditioning Modulates the Peripheral Innate Immune System to Promote Anti-Inflammatory and Protective Responses in Mice Subjected to Focal Cerebral Ischemia.Front Immunol. 2022 Mar 11;13:825834. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.825834. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35359933 Free PMC article.
-
Transformation of A1/A2 Astrocytes Participates in Brain Ischemic Tolerance Induced by Cerebral Ischemic Preconditioning via Inhibiting NDRG2.Neurochem Res. 2024 Jul;49(7):1665-1676. doi: 10.1007/s11064-024-04134-8. Epub 2024 Feb 27. Neurochem Res. 2024. PMID: 38411782
-
Ischemic preconditioning provides long-lasting neuroprotection against ischemic stroke: The role of Nrf2.Exp Neurol. 2020 Mar;325:113142. doi: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2019.113142. Epub 2019 Dec 5. Exp Neurol. 2020. PMID: 31812555 Free PMC article.
-
Focal cerebral ischemic tolerance and change in blood-brain barrier permeability after repetitive pure oxygen exposure preconditioning in a rodent model.J Neurosurg. 2016 Oct;125(4):943-952. doi: 10.3171/2015.7.JNS142220. Epub 2016 Jan 29. J Neurosurg. 2016. PMID: 26824373
Cited by
-
Exploring the Frontiers of Neuroinflammation: New Horizons in Research and Treatment.Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2024 Oct 19;46(10):11665-11667. doi: 10.3390/cimb46100692. Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2024. PMID: 39451572 Free PMC article.
-
TSG-6 Protects Against Cerebral Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury via Upregulating Hsp70-1B in Astrocytes.CNS Neurosci Ther. 2025 Mar;31(3):e70354. doi: 10.1111/cns.70354. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2025. PMID: 40130432 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Martin S.S., Aday A.W., Almarzooq Z.I., Anderson C.A.M., Arora P., Avery C.L., Baker-Smith C.M., Barone Gibbs B., Beaton A.Z., Boehme A.K., et al. 2024 Heart Disease and Stroke Statistics: A Report of US and Global Data from the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2024;149:e347–e913. doi: 10.1161/CIR.0000000000001209. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Steinmetz J.D., Seeher K.M., Schiess N., Nichols E., Cao B., Servili C., Cavallera V., Cousin E., Hagins H., Moberg M.E., et al. Global, Regional, and National Burden of Disorders Affecting the Nervous System, 1990–2021: A Systematic Analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2021. Lancet Neurol. 2024;23:344–381. doi: 10.1016/S1474-4422(24)00038-3. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Mehta A., Fifi J.T., Shoirah H., Singh I.P., Shigematsu T., Kellner C.P., De Leacy R., Mocco J., Majidi S. National Trends in Utilization and Outcome of Endovascular Thrombectomy for Acute Ischemic Stroke in Elderly. J. Stroke Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2021;30:105505. doi: 10.1016/j.jstrokecerebrovasdis.2020.105505. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Ramos-Araque M.E., Rodriguez C., Vecino R., Cortijo Garcia E., de Lera Alfonso M., Sanchez Barba M., Colàs-Campàs L., Purroy F., Arenillas J.F., Almeida A., et al. The Neuronal Ischemic Tolerance Is Conditioned by the Tp53 Arg72Pro Polymorphism. Transl. Stroke Res. 2019;10:204–215. doi: 10.1007/s12975-018-0631-1. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

