Hyaluronic Acid in Nanopharmaceuticals: An Overview
- PMID: 39329973
- PMCID: PMC11431703
- DOI: 10.3390/cimb46090621
Hyaluronic Acid in Nanopharmaceuticals: An Overview
Abstract
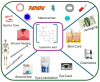
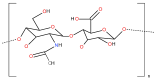
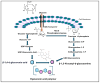
Hyaluronic acid (HA) is a naturally occurring, long, unbranched polysaccharide that plays a critical role in maintaining skin structure and hydration. Its unique properties make it a valuable component in the field of nanopharmaceuticals. The combination of HA into nanopharmaceuticals enhances its ability to interact with various therapeutic agents, improving the delivery and efficacy of drugs. HA-based nanoparticles, including solid lipid nanoparticles, and polymeric nanogels, offer controlled release, enhanced stability, and targeted delivery of therapeutic agents. These innovations significantly improve therapeutic outcomes and reduce side effects, making HA an essential tool in modern medicine. In general, HA-modified liposomes enhance drug encapsulation and targeting, while HA-modified solid lipid nanoparticles (SLNs) provide a solid lipid core for drug encapsulation, offering controlled release and stability. This article provides an overview of the potential applications and recent advancements of HA in nanopharmaceuticals, emphasizing its significant impact on the evolving field of targeted drug delivery and advanced therapeutic strategies. By delving into the unique properties of HA and its compatibility with various therapeutic agents, this review underscores the promising potential of HA in revolutionizing nanopharmaceuticals.
Keywords: hyaluronic acid; lubricant; nanopharmaceuticals; nanotechnology.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Hyaluronic acid-coated solid lipid nanoparticles enhance antirheumatic activity and reduce toxicity of methotrexate.Nanomedicine (Lond). 2022 Jul;17(16):1099-1114. doi: 10.2217/nnm-2022-0009. Epub 2022 Sep 30. Nanomedicine (Lond). 2022. PMID: 36178114
-
Advancements in the use of nanopharmaceuticals for cancer treatment.J Oncol Pharm Pract. 2024 Sep;30(6):1078-1083. doi: 10.1177/10781552241251757. Epub 2024 May 5. J Oncol Pharm Pract. 2024. PMID: 38706188 Review.
-
Efficient delivery of curcumin by functional solid lipid nanoparticles with promoting endosomal escape and liver targeting properties.Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2024 Dec;244:114177. doi: 10.1016/j.colsurfb.2024.114177. Epub 2024 Aug 27. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2024. PMID: 39217729
-
Recent Advancements in Nanopharmaceuticals for Novel Drug Delivery Systems.Pharm Nanotechnol. 2025;13(2):271-286. doi: 10.2174/0122117385324246240826042254. Pharm Nanotechnol. 2025. PMID: 39323341 Review.
-
Hyaluronic acid-coated solid lipid nanoparticles for targeted delivery of vorinostat to CD44 overexpressing cancer cells.Carbohydr Polym. 2014 Dec 19;114:407-415. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2014.08.026. Epub 2014 Aug 23. Carbohydr Polym. 2014. PMID: 25263908
Cited by
-
Formation and evaluation of doxorubicin and cromoglycate metal-organic framework for anti-cancer activity.Nanomedicine (Lond). 2025 Mar;20(5):467-479. doi: 10.1080/17435889.2025.2459059. Epub 2025 Jan 31. Nanomedicine (Lond). 2025. PMID: 39888613
-
Editorial for Special Issue "Effects of Nanoparticles on Living Organisms 2.0".Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2025 Jan 13;47(1):46. doi: 10.3390/cimb47010046. Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2025. PMID: 39852161 Free PMC article.
-
Polysaccharide-Based Nanocarriers for Natural Antimicrobials: A Review.Polymers (Basel). 2025 Jun 24;17(13):1750. doi: 10.3390/polym17131750. Polymers (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40647761 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Acetazolamide-Loaded Nanoparticle Based on Modified Hyaluronic Acid as Delivery System to Target Carbonic Anhydrases in Escherichia coli.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 May 20;26(10):4908. doi: 10.3390/ijms26104908. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40430049 Free PMC article.
-
Hyaluronic Acid and Skin: Its Role in Aging and Wound-Healing Processes.Gels. 2025 Apr 9;11(4):281. doi: 10.3390/gels11040281. Gels. 2025. PMID: 40277717 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Salih A.R.C., Farooqi H.M.U., Amin H., Karn P.R., Meghani N., Nagendran S. Hyaluronic acid: Comprehensive review of a multifunctional biopolymer. Futur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2024;10:63. doi: 10.1186/s43094-024-00636-y. - DOI
-
- De Lucia O., Murgo A., Pregnolato F., Pontikaki I., De Souza M., Sinelli A., Cimaz R., Caporali R. Hyaluronic Acid Injections in the Treatment of Osteoarthritis Secondary to Primary In-flammatory Rheumatic Diseases: A Systematic Review and Qualitative Synthesis. Adv. Ther. 2020;37:1347–1359. doi: 10.1007/s12325-020-01256-7. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources