Complete Blood Count-Based Biomarkers as Predictors of Clinical Outcomes in Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Patients with PD-L1 < 50% Treated with First-Line Chemoimmunotherapy
- PMID: 39329995
- PMCID: PMC11431676
- DOI: 10.3390/curroncol31090367
Complete Blood Count-Based Biomarkers as Predictors of Clinical Outcomes in Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Patients with PD-L1 < 50% Treated with First-Line Chemoimmunotherapy
Abstract
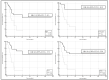
Background: The aim of the study was to investigate a series of complete blood cell count-based biomarkers of systemic inflammation as predictors of clinical outcomes in patients who underwent first-line chemoimmunotherapy for advanced NSCLC. Methods: Consecutive patients with pathologically diagnosed stage III/IV NSCLC and PD-L1 < 50% who underwent first-line chemoimmunotherapy were retrospectively enrolled. The clinical outcomes used for biomarker evaluation were Objective Response Rate (ORR) and Overall Survival (OS). Results: Non-responders had significantly higher values of neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio (NLR, median: 5.36; IQR: 2.78-10.82 vs. 3.31; IQR: 2.15-4.12, p = 0.019), neutrophil to monocyte ratio (NMR, median: 14.00; IQR: 8.82-21.20 vs. 9.20; IQR: 7.45-11.20, p = 0.013), and systemic inflammation index (SII, median: 1395; IQR: 929-3334 vs. 945; IQR: 552-1373, p = 0.025), but only NLR and NMR remained independently associated with clinical response in multivariate logistic regression. In the univariate analysis, white blood cells (OR:1.2202; 95% CI: 1.0339-1.4400, p = 0.019), neutrophils (OR:1.2916; 95% CI: 1.0692-1.5604, p = 0.008), NLR (OR:1.3601: 95% CI: 1.0949-1.6896, p = 0.005) and NMR (OR:1.2159; 95% CI: 1.00396-1.4221, p = 0.015) were significantly associated with survival; Cox regression models confirmed that neutrophils, NLR, and MLR were independently associated with survival; NLR, at a cut-off value of 4.0, showed the better AUC (0.749) in predicting OS. Conclusions: Baseline complete blood cell count biomarkers, especially the NLR, can predict clinical outcomes in patients with advanced NSCLC treated with first-line chemoimmunotherapy.
Keywords: MNR; NLR; biomarkers; blood cell count; chemotherapy; immunotherapy; lung cancer.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- International Agency for Research on Cancer Global Cancer Observatory: Cancer Today. Lyon, France. [(accessed on 8 May 2024)]. Available online: https://gco.iarc.who.int/media/globocan/factsheets/cancers/15-trachea-br....
-
- Colombino M., Paliogiannis P., Cossu A., Santeufemia D.A., Sardinian Lung Cancer (SLC) Study Group. Sini M.C., Casula M., Palomba G., Manca A., Pisano M., et al. EGFR, KRAS, BRAF, ALK, and cMET genetic alterations in 1440 Sardinian patients with lung adenocarcinoma. BMC Pulm. Med. 2019;19:209. doi: 10.1186/s12890-019-0964-x. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- De Koning H.J., van der Aalst C.M., de Jong P.A., Scholten E.T., Nackaerts K., Heuvelmans M.A., Lammers J.J., Weenink C., Yousaf-Khan U., Horeweg N., et al. Reduced lung-cancer mortality with volume CT screening in a randomized trial. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020;382:503–513. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1911793. - DOI - PubMed
-
- National Comprehensive Cancer Network. [(accessed on 8 May 2024)]. Available online: https://www.nccn.org/professionals/physician_gls/pdf/nscl.pdf.
-
- Hendriks L.E., Kerr K.M., Menis J., Mok T.S., Nestle U., Passaro A., Peters S., Planchard D., Smit E.F., Solomon B.J., et al. Non-oncogene-addicted metastatic non-small-cell lung cancer: ESMO Clinical Practice Guideline for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann. Oncol. 2023;34:358–376. doi: 10.1016/j.annonc.2022.12.013. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials