Developing an Early Warning System for Financial Networks: An Explainable Machine Learning Approach
- PMID: 39330129
- PMCID: PMC11432077
- DOI: 10.3390/e26090796
Developing an Early Warning System for Financial Networks: An Explainable Machine Learning Approach
Abstract
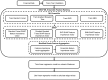
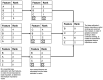
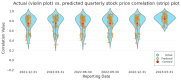
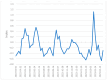
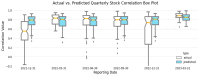
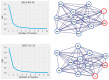
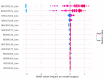
Identifying the influential variables that provide early warning of financial network instability is challenging, in part due to the complexity of the system, uncertainty of a failure, and nonlinear, time-varying relationships between network participants. In this study, we introduce a novel methodology to select variables that, from a data-driven and statistical modeling perspective, represent these relationships and may indicate that the financial network is trending toward instability. We introduce a novel variable selection methodology that leverages Shapley values and modified Borda counts, in combination with statistical and machine learning methods, to create an explainable linear model to predict relationship value weights between network participants. We validate this new approach with data collected from the March 2023 Silicon Valley Bank Failure. The models produced using this novel method successfully identified the instability trend using only 14 input variables out of a possible 3160. The use of parsimonious linear models developed by this method has the potential to identify key financial stability indicators while also increasing the transparency of this complex system.
Keywords: complex systems; machine learning; macroprudential economics; systemic risk.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Alessi L., Detken C. Identifying excessive credit growth and leverage. J. Financ. Stab. 2018;35:215–225. doi: 10.1016/j.jfs.2017.06.005. - DOI
-
- Alessi L., Savona R. Machine learning for financial stability. In: Consoli S., Recupero D.R., Saisana M., editors. Data Science for Economics and Finance: Methodologies and Applications. Springer; Cham, Switzerland: 2021. pp. 65–87. - DOI
-
- Buckman M., Joseph A., Robertson H. Data Science for Economics and Finance Methodologies and Applications. Springer; Cham, Switzerland: 2021. Opening the Black Box: Machine Learning Interpretability and Inference Tools with an Application to Economic Forecasting; pp. 43–61. - DOI
-
- Tung H.K.K., Wong M.C.S. Financial risk forecasting with nonlinear dynamics and support vector regression. J. Oper. Res. Soc. 2009;60:685–695. doi: 10.1057/palgrave.jors.2602594. - DOI
-
- Shannon C.E. Mathematical theory of communication. Bell Syst. Tech. J. 1948;27:306–317. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

