Application of the Self-Assembling Peptide Hydrogel RADA16 for Hemostasis during Tonsillectomy: A Feasibility Study
- PMID: 39330246
- PMCID: PMC11432850
- DOI: 10.3390/jfb15090271
Application of the Self-Assembling Peptide Hydrogel RADA16 for Hemostasis during Tonsillectomy: A Feasibility Study
Abstract
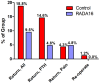
Tonsillectomy is a common surgical procedure but carries a high risk of readmission for secondary bleeding and pain. This study evaluated the feasibility and effectiveness of using the hemostatic self-assembling peptide hydrogel RADA16 (PuraBond, 3-D Matrix SAS; Caluire et Cuire, France) to control bleeding from the tonsillectomy wound bed. Readmission/re-operation rates were compared between a prospective case series of 21 primarily adult tonsillectomy patients treated with topical RADA16 and an untreated historical Control group of 164 patients who underwent tonsillectomy by 10 surgeons at a single tertiary hospital in the UK between March 2019 and June 2022. Cumulative readmission rates for any reason were 2-fold elevated in Control subjects (18.9%; n = 31/164 subjects) compared to patients treated intra-operatively with RADA16 hemostatic hydrogel (9.5%; n = 2/21) (p = 0.378). Readmission rates for postoperative bleeding were 3-fold higher in Controls (14.6%; n = 24/164 subjects) than in the RADA16-treated group (4.8%; n = 1/21) (p = 0.317). A similar rate of retreatment for pain was recorded in the Control (4.3%; n = 7/164) and RADA16 (4.8%; n = 1/21) groups (p = 0.999). Two Control subjects (1.2%) required re-operation for recalcitrant bleeding; no RADA16 subject (0.0%) required re-operation for any reason. No device-related adverse events occurred in the RADA16 group. Surgeons were pleased with the easy learning curve and technical feasibility associated with intra-operatively administering RADA16 hemostatic hydrogel. Intra-operative hemostasis using RADA16 peptide hydrogel was straightforward and was associated with a trend of 3-fold lower rates of readmission for postoperative bleeding events than untreated Control subjects.
Keywords: RADA16; bleeding; hemostasis; hydrogel; re-operation; readmission; tonsillectomy; wound healing.
Conflict of interest statement
Test article was provided by 3-D Matrix, Inc. JM received consultancy fees from 3-D Matrix. All authors report no other potential conflict of interest, financial or otherwise. The sponsors had no role in the design, execution, interpretation, or writing of the study.
Figures
References
-
- Ear M.A. Nose & Throat Surgery: GIRFT Programme National Specialty Report, National Health Services UK. 2019. [(accessed on 26 August 2024)]. Available online: https://gettingitrightfirsttime.co.uk/wp-content/uploads/2019/12/ENT-Rep....
-
- Wilson J.A., O’Hara J., Fouweather T., Homer T., Stocken D.D., Vale L., Haighton C., Rousseau N., Wilson R., McSweeney L., et al. Conservative management versus tonsillectomy in adults with recurrent acute tonsillitis in the UK (NATTINA): A multicentre, open-label, randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2023;401:2051–2059. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(23)00519-6. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Sankar S., O’Neill K., Bagot D’Arc M., Rebeca F., Buffier M., Aleksi E., Fan M., Matsuda N., Gil E.S., Spirio L. Clinical Use of the Self-Assembling Peptide RADA16: A Review of Current and Future Trends in Biomedicine. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2021;9:679525. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2021.679525. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

