Recent Advances in Anti-Inflammatory Compounds from Marine Microorganisms
- PMID: 39330305
- PMCID: PMC11433063
- DOI: 10.3390/md22090424
Recent Advances in Anti-Inflammatory Compounds from Marine Microorganisms
Abstract
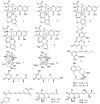
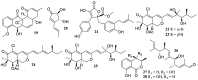
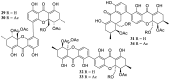
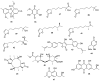
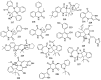
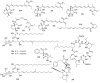
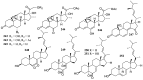
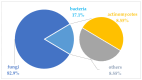
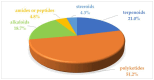
Marine microbial secondary metabolites with diversified structures have been found as promising sources of anti-inflammatory lead compounds. This review summarizes the sources, chemical structures, and pharmacological properties of anti-inflammatory natural products reported from marine microorganisms in the past three years (2021-2023). Approximately 252 anti-inflammatory compounds, including 129 new ones, were predominantly obtained from marine fungi and they are structurally divided into polyketides (51.2%), terpenoids (21.0%), alkaloids (18.7%), amides or peptides (4.8%), and steroids (4.3%). This review will shed light on the development of marine microbial secondary metabolites as potential anti-inflammatory lead compounds with promising clinical applications in human health.
Keywords: anti-inflammatory compounds; chemical structures; marine microorganisms; secondary metabolites; structure–activity relationship.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Novel Bioactive Natural Products from Marine-Derived Penicillium Fungi: A Review (2021-2023).Mar Drugs. 2024 Apr 23;22(5):191. doi: 10.3390/md22050191. Mar Drugs. 2024. PMID: 38786582 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Comprehensive Review of Bioactive Peptides from Marine Fungi and Their Biological Significance.Mar Drugs. 2019 Sep 29;17(10):559. doi: 10.3390/md17100559. Mar Drugs. 2019. PMID: 31569458 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Natural Products from Marine-Derived Fungi with Anti-Inflammatory Activity.Mar Drugs. 2024 Sep 25;22(10):433. doi: 10.3390/md22100433. Mar Drugs. 2024. PMID: 39452841 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Anti-Vibrio potential of natural products from marine microorganisms.Eur J Med Chem. 2023 Apr 5;252:115330. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2023.115330. Epub 2023 Mar 29. Eur J Med Chem. 2023. PMID: 37011553 Review.
-
Origins, Structures, and Bioactivities of Secondary Metabolites from Marine-derived Penicillium Fungi.Mini Rev Med Chem. 2021;21(15):2000-2019. doi: 10.2174/1389557521666210217093517. Mini Rev Med Chem. 2021. PMID: 33596801
Cited by
-
Multifaceted Marine Peptides and Their Therapeutic Potential.Mar Drugs. 2025 Jul 15;23(7):288. doi: 10.3390/md23070288. Mar Drugs. 2025. PMID: 40710513 Free PMC article. Review.
-
New Pyridinium Compound from Marine Sediment-Derived Bacterium Bacillus licheniformis S-1.Molecules. 2024 Dec 24;30(1):7. doi: 10.3390/molecules30010007. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 39795066 Free PMC article.
-
Lipotrichaibol A and Trichoderpeptides A-D: Five New Peptaibiotics from a Sponge-Derived Trichoderma sp. GXIMD 01001.Mar Drugs. 2025 Jun 24;23(7):264. doi: 10.3390/md23070264. Mar Drugs. 2025. PMID: 40710489 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

