Development of a Multiplex Real-Time PCR Assay for the Simultaneous Detection of Two Fungal Pathogens Causing Pneumonia
- PMID: 39330379
- PMCID: PMC11433024
- DOI: 10.3390/jof10090619
Development of a Multiplex Real-Time PCR Assay for the Simultaneous Detection of Two Fungal Pathogens Causing Pneumonia
Abstract
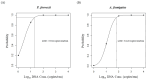
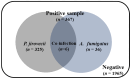
Infectious diseases caused by fungal sources are of great interest owing to their increasing prevalence. Invasive fungal infections, including invasive pulmonary aspergillosis caused by Aspergillus fumigatus, and Pneumocystis pneumonia caused by Pneumocystis jirovecii, are significant causes of morbidity and mortality among immunocompromised patients. The accurate and timely detection of these pathogens in this high-risk population is crucial for effective patient management. We developed a multiplex real-time polymerase chain reaction (PCR) assay, RF2 mRT-PCR, specifically designed to detect two respiratory fungi, P. jirovecii and A. fumigatus, and evaluated its performance in specimens of patients with lower respiratory tract infection. The performance was evaluated using 731 clinical samples, 55 reference species, and one synthetic DNA. The reproducibility test yielded a probit curve with a lower limit of detection of 19.82 copies/reaction for P. jirovecii and 64.20 copies/reaction for A. fumigatus. The RF2 mRT-PCR assay did not cross-react with non-A. fumigatus Aspergillus species or other common bacterial and viral species, and showed 100% in vitro sensitivity and specificity with reference assays. Additionally, it simultaneously detected A. fumigatus and P. jirovecii in co-infected samples. Therefore, the RF2 mRT-PCR assay is an efficient and reliable tool for in vitro diagnosis of A. fumigatus and P. jirovecii pulmonary infections.
Keywords: Aspergillus fumigatus; Pneumocystis jirovecii; diagnostic accuracy study; fungal respiratory infection; molecular diagnostics; multiplex real-time PCR.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Evaluation of the Performance of a Multiplex Real-Time PCR Assay for the Identification of Aspergillus, Cryptococcus neoformans, and Pneumocystis jirovecii Simultaneously from Sputum in Multicenter.Infect Drug Resist. 2022 Oct 18;15:6009-6017. doi: 10.2147/IDR.S379043. eCollection 2022. Infect Drug Resist. 2022. PMID: 36267265 Free PMC article.
-
Multiplex Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction on Sputum for the Diagnosis of Pneumocystis jirovecii Pneumonia in Children: A Retrospective Study.Infect Drug Resist. 2021 Sep 7;14:3627-3635. doi: 10.2147/IDR.S326814. eCollection 2021. Infect Drug Resist. 2021. PMID: 34522105 Free PMC article.
-
Development of a multiplex real-time PCR assay for the simultaneous detection of four bacterial pathogens causing pneumonia.PLoS One. 2021 Jun 17;16(6):e0253402. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0253402. eCollection 2021. PLoS One. 2021. PMID: 34138947 Free PMC article.
-
Pulmonary co-infections by Pneumocystis jirovecii and Aspergillus fumigatus in non-HIV patients: A report of two cases and literature review.Mycoses. 2017 Oct;60(10):626-633. doi: 10.1111/myc.12642. Epub 2017 Jun 28. Mycoses. 2017. PMID: 28660636 Review.
-
Molecular diagnosis and epidemiology of fungal infections.Med Mycol. 1998;36 Suppl 1:249-57. Med Mycol. 1998. PMID: 9988514 Review.
References
-
- World Health Organization (WHO) Report WHO Fungal Priority Pathogens List to Guide Research, Development and Public Health Action. 2022. [(accessed on 4 June 2024)]. Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789240060241.
-
- Harris J.R., Balajee S.A., Park B.J. Pneumocystis Jirovecii Pneumonia: Current Knowledge and Outstanding Public Health Issues. Curr. Fungal Infect. Rep. 2010;4:229–237. doi: 10.1007/s12281-010-0029-3. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

