Metabolomic Effects of Liraglutide Therapy on the Plasma Metabolomic Profile of Patients with Obesity
- PMID: 39330507
- PMCID: PMC11433991
- DOI: 10.3390/metabo14090500
Metabolomic Effects of Liraglutide Therapy on the Plasma Metabolomic Profile of Patients with Obesity
Abstract
Background: Liraglutide, a long-acting glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist (GLP1RA), is a well-established anti-diabetic drug, has also been approved for the treatment of obesity at a dose of 3 mg. There are a limited number of studies in the literature that have looked at changes in metabolite levels before and after liraglutide treatment in patients with obesity. To this end, in the present study we aimed to explore the changes in the plasma metabolomic profile, using liquid chromatography-high resolution mass spectrometry (LC-HRMS) in patients with obesity.
Methods: A single-center prospective study was undertaken to evaluate the effectiveness of 3 mg liraglutide therapy in twenty-three patients (M/F: 8/15) with obesity, mean BMI 40.81 ± 5.04 kg/m2, and mean age of 36 ± 10.9 years, in two groups: at baseline (pre-treatment) and after 12 weeks of treatment (post-treatment). An untargeted metabolomic profiling was conducted in plasma from the pre-treatment and post-treatment groups using LC-HRMS, along with bioinformatics analysis using ingenuity pathway analysis (IPA).
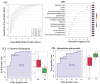
Results: The metabolomics analysis revealed a significant (FDR p-value ≤ 0.05, FC 1.5) dysregulation of 161 endogenous metabolites (97 upregulated and 64 downregulated) with distinct separation between the two groups. Among the significantly dysregulated metabolites, the majority of them were identified as belonging to the class of oxidized lipids (oxylipins) that includes arachidonic acid and its derivatives, phosphorglycerophosphates, N-acylated amino acids, steroid hormones, and bile acids. The biomarker analysis conducted using MetaboAnalyst showed PGP (a21:0/PG/F1alpha), an oxidized lipid, as the first metabolite among the list of the top 15 biomarkers, followed by cysteine and estrone. The IPA analysis showed that the dysregulated metabolites impacted the pathway related to cell signaling, free radical scavenging, and molecular transport, and were focused around the dysregulation of NF-κB, ERK, MAPK, PKc, VEGF, insulin, and pro-inflammatory cytokine signaling pathways.
Conclusions: The findings suggest that liraglutide treatment reduces inflammation and modulates lipid metabolism and oxidative stress. Our study contributes to a better understanding of the drug's multifaceted impact on overall metabolism in patients with obesity.
Keywords: arachidonic acid; biomarkers; liraglutide; mass spectrometry; metabolomics; obesity; oxidized lipids.
Conflict of interest statement
A.A.A. has received research funding from the Ministry of Education in Saudi Arabia, King Saud University, King Abdulaziz City for Science and Technology, Hevolution Foundation and Dallah Hospital. A.A.A. has received honoraria for lectures and scientific consultations from Novo Nordisk and Eli Lilly. A.A.A. has received financial support to attend scientific conferences from Novo Nordisk. A.D.M. has received research funding from the MRC, NIHR, Jon Moulton Charitable Foundation, Anabio, Fractyl, Boehringer Ingelheim, Gila, Randox, and Novo Nordisk. A.D.M. has received honoraria for lectures and presentations from Novo Nordisk, Astra Zeneca, Currax Pharmaceuticals, Boehringer Ingelheim, Screen Health, GI Dynamics, Algorithm, Eli Lilly, Ethicon, and Medtronic. ADM is a shareholder in the Beyond BMI clinic, which provides clinical obesity care. The remaining authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Label-free quantitative proteomic profiling reveals differential plasma protein expression in patients with obesity after treatment with liraglutide.Front Mol Biosci. 2024 Sep 11;11:1458675. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2024.1458675. eCollection 2024. Front Mol Biosci. 2024. PMID: 39324112 Free PMC article.
-
Early metabolomic, lipid and lipoprotein changes in response to medical and surgical therapeutic approaches to obesity.Metabolism. 2023 Jan;138:155346. doi: 10.1016/j.metabol.2022.155346. Epub 2022 Nov 12. Metabolism. 2023. PMID: 36375643 Clinical Trial.
-
Pharmacometabolomic profiles in type 2 diabetic subjects treated with liraglutide or glimepiride.Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2021 Dec 17;20(1):237. doi: 10.1186/s12933-021-01431-2. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2021. PMID: 34920733 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Liraglutide: A New Option for the Treatment of Obesity.Pharmacotherapy. 2015 Oct;35(10):926-34. doi: 10.1002/phar.1639. Pharmacotherapy. 2015. PMID: 26497479 Review.
-
Liraglutide: A Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 Agonist for Chronic Weight Management.Consult Pharm. 2016 Dec 1;31(12):685-697. doi: 10.4140/TCP.n.2016.685. Consult Pharm. 2016. PMID: 28074747 Review.
Cited by
-
Clinical studies on anti-obesity medications in Arab countries.Saudi Med J. 2025 May;46(5):459-477. doi: 10.15537/smj.2025.46.5.20250126. Saudi Med J. 2025. PMID: 40335111 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Powell-Wiley T.M., Poirier P., Burke L.E., Despres J.P., Gordon-Larsen P., Lavie C.J., Lear S.A., Ndumele C.E., Neeland I.J., Sanders P., et al. Obesity and Cardiovascular Disease: A Scientific Statement from the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2021;143:e984–e1010. doi: 10.1161/CIR.0000000000000973. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Alshehri A., AlFaris N., Al Qahtani A.M., Shams M., Yahia M. Clinical effectiveness of Liraglutide 3.0 mg and impact of weight loss in improving obesity-related comorbid conditions in King Fahad Medical City, Kingdom of Saudi Arabia: A real-world experience. Clin. Obes. 2023;13:e12594. doi: 10.1111/cob.12594. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Park J.H., Kim J.Y., Choi J.H., Park H.S., Shin H.Y., Lee J.M., Kim J.W., Ko H.J., Chon S., Kim B.K., et al. Effectiveness of liraglutide 3 mg for the treatment of obesity in a real-world setting without intensive lifestyle intervention. Int. J. Obes. 2021;45:776–786. doi: 10.1038/s41366-021-00739-z. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

