Temporal Variation and Industry-Specific Differences of the Use of Volatile Organic Compounds from 2018 to 2023 and Their Health Risks in a Typical Industrially Concentrated Area in South China
- PMID: 39330562
- PMCID: PMC11436172
- DOI: 10.3390/toxics12090634
Temporal Variation and Industry-Specific Differences of the Use of Volatile Organic Compounds from 2018 to 2023 and Their Health Risks in a Typical Industrially Concentrated Area in South China
Abstract
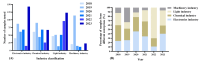
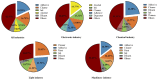
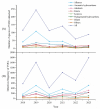
The risk of occupational exposure to organic solvents varies across industries due to factors such as processing materials, ventilation conditions, and exposure duration. Given the dynamic nature of organic solvent use and occupational exposures, continuous monitoring and analysis are essential for identifying high-risk hazards and developing targeted prevention strategies. Therefore, this study aims to analyze the use of organic solvents and volatile organic compounds (VOCs) in different industries in Bao'an District, Shenzhen, China, from 2018 to 2023, to understand their temporal variation and industry-specific differences and to identify high-risk occupational hazards. This study includes 1335 organic solvent samples, used by 414 different industry enterprises, and 1554 air samples. The result shows that the usage of organic solvents in various industries decreased with the outbreak of the pandemic and, conversely, increased as the situation improved. The most frequently detected volatile components in organic solvents were alkanes, followed by aromatic hydrocarbons. The ratios of the detection frequency of VOCs to the total number of detected categories increased year by year after 2020, indicating a tendency towards reduction and concentration of the types of organic solvents used in industrial production. Among the 8 high-risk VOCs, toluene (22.5%), n-hexane (22.0%), xylene (16.1%), and ethylbenzene (15.3%) have relatively high detection rates, suggesting that they need to be focused on in occupational health. Through air samples, the results show that trichloroethylene and xylene pose a high risk to human health (HQ > 1). We recommend that industry should strengthen monitoring of these two VOCs.
Keywords: Shenzhen; industries; occupational hazards; organic solvents.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
Similar articles
-
[Analysis of volatile organic components of organic solvents used in Bao'an District of Shenzhen].Zhonghua Lao Dong Wei Sheng Zhi Ye Bing Za Zhi. 2022 Nov 20;40(11):867-871. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn121094-20210720-00361. Zhonghua Lao Dong Wei Sheng Zhi Ye Bing Za Zhi. 2022. PMID: 36510726 Chinese.
-
[Emission Characteristics and Risk Assessment of Volatile Organic Compounds from Typical Factories in Zhengzhou].Huan Jing Ke Xue. 2020 Jul 8;41(7):3056-3065. doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.201911106. Huan Jing Ke Xue. 2020. PMID: 32608877 Chinese.
-
[Source Profiles and Impact of Volatile Organic Compounds in Typical Industries in Luohe City].Huan Jing Ke Xue. 2024 Aug 8;45(8):4484-4492. doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.202308177. Huan Jing Ke Xue. 2024. PMID: 39168668 Chinese.
-
[Emission Characteristics and Characteristic Substance Identification of Volatile Odorous Organic Compounds in Industries Using Organic Solvents].Huan Jing Ke Xue. 2018 Aug 8;39(8):3557-3562. doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.201711012. Huan Jing Ke Xue. 2018. PMID: 29998661 Chinese.
-
[High-resolution Emission Inventory of Reactive Volatile Organic Compounds from Anthropogenic Sources in the Yangtze River Delta Region].Huan Jing Ke Xue. 2023 Jan 8;44(1):58-65. doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.202201100. Huan Jing Ke Xue. 2023. PMID: 36635795 Chinese.
References
-
- Joshi D.R., Adhikari N. An Overview on Common Organic Solvents and Their Toxicity. J. Pharm. Res. Int. 2019;28:1–18. doi: 10.9734/jpri/2019/v28i330203. - DOI
-
- Mo Z., Cui R., Yuan B., Cai H., McDonald B.C., Li M., Zheng J., Shao M. A Mass-Balance-Based Emission Inventory of Non-Methane Volatile Organic Compounds (NMVOCs) for Solvent Use in China. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2021;21:13655–13666. doi: 10.5194/acp-21-13655-2021. - DOI
-
- Stockwell C.E., Coggon M.M., Gkatzelis G.I., Ortega J., McDonald B.C., Peischl J., Aikin K., Gilman J.B., Trainer M., Warneke C. Volatile Organic Compound Emissions from Solvent- and Water-Borne Coatings—Compositional Differences and Tracer Compound Identifications. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2021;21:6005–6022. doi: 10.5194/acp-21-6005-2021. - DOI
-
- Sheldon R.A. Green Solvents for Sustainable Organic Synthesis: State of the Art. Green Chem. 2005;7:267–278. doi: 10.1039/b418069k. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources