Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotubes Accelerate Leukaemia Development in a Mouse Model
- PMID: 39330574
- PMCID: PMC11435454
- DOI: 10.3390/toxics12090646
Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotubes Accelerate Leukaemia Development in a Mouse Model
Erratum in
-
Correction: Wang et al. Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotubes Accelerate Leukaemia Development in a Mouse Model. Toxics 2024, 12, 646.Toxics. 2024 Nov 18;12(11):823. doi: 10.3390/toxics12110823. Toxics. 2024. PMID: 39591013 Free PMC article.
Abstract
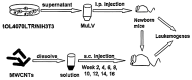
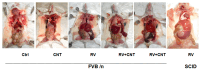
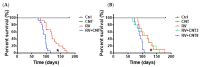
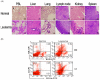
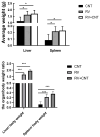
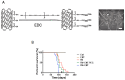
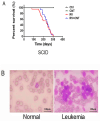
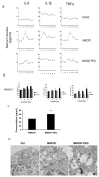
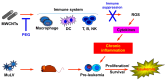
Inflammation is associated with an increased risk of developing various cancers in both animals and humans, primarily solid tumors but also myeloproliferative neoplasms (MPNs), myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS), and acute myeloid leukemia (AML). Multi-walled carbon nanotubes (MWCNTs), a type of carbon nanotubes (CNTs) increasingly used in medical research and other fields, are leading to a rising human exposure. Our study demonstrated that exposing mice to MWCNTs accelerated the progression of spontaneous MOL4070LTR virus-induced leukemia. Additionally, similar exposures elevated pro-inflammatory cytokines such as interleukin (IL)-1β, IL-6, and tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α and induced reactive oxygen species (ROS) in a murine macrophage cell line. These effects were significantly reduced in immunodeficient mice and when mice were treated with methoxypolyethylene glycol amine (PEG)-modified MWCNTs. These findings underscore the necessity of evaluating the safety of MWCNTs, particularly for those with hematologic cancers.
Keywords: MOL4070LTR; PEG; inflammation; leukemia; multi-walled carbon nanotubes.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Shi H.K., Carter S., Haines N.L. Harvesting electrical energy from carbon nanotube yarn twist. Science. 2017;357:773–778. - PubMed
-
- Lima M.D., Li N., Jung de Andrade M., Fang S., Oh J., Spinks G.M., Kozlov M.E., Haines C.S., Suh D., Foroughi J., et al. Electrically, Chemically, and Photonically Powered Torsional and Tensile Actuation of Hybrid Carbon Nanotube Yarn Muscles. Science. 2012;338:928–932. doi: 10.1126/science.1226762. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

