The Contrasting Effects of Bothrops lanceolatus and Bothrops atrox Venom on Procoagulant Activity and Thrombus Stability under Blood Flow Conditions
- PMID: 39330858
- PMCID: PMC11435654
- DOI: 10.3390/toxins16090400
The Contrasting Effects of Bothrops lanceolatus and Bothrops atrox Venom on Procoagulant Activity and Thrombus Stability under Blood Flow Conditions
Abstract
Background: Consumption coagulopathy and hemorrhagic syndrome are the typical features of Bothrops sp. snake envenoming. In contrast, B. lanceolatus envenoming can induce thrombotic complications. Our aim was to test whether crude B. lanceolatus and B. atrox venoms would display procoagulant activity and induce thrombus formation under flow conditions.
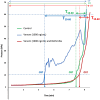
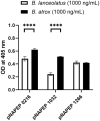
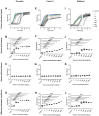
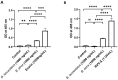
Methods and principal findings: Fibrin formation in human plasma was observed for B. lanceolatus venom at 250-1000 ng/mL concentrations, which also induced clot formation in purified human fibrinogen, indicating thrombin-like activity. The degradation of fibrinogen confirmed the fibrinogenolytic activity of B. lanceolatus venom. B. lanceolatus venom displayed consistent thrombin-like and kallikrein-like activity increases in plasma conditions. The well-known procoagulant B. atrox venom activated plasmatic coagulation factors in vitro and induced firm thrombus formation under high shear rate conditions. In contrast, B. lanceolatus venom induced the formation of fragile thrombi that could not resist shear stress.
Conclusions: Our results suggest that crude B. lanceolatus venom displays amidolytic activity and can activate the coagulation cascade, leading to prothrombin activation. B. lanceolatus venom induces the formation of an unstable thrombus under flow conditions, which can be prevented by the specific monovalent antivenom Bothrofav®.
Keywords: B. atrox; B. lanceolatus; Bothrops snake envenoming; antivenom; kallikrein; procoagulant; shear stress; thrombin; thrombosis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures






Similar articles
-
A murine experimental model of the pulmonary thrombotic effect induced by the venom of the snake Bothrops lanceolatus.PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2024 Oct 2;18(10):e0012335. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0012335. eCollection 2024 Oct. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2024. PMID: 39356725 Free PMC article.
-
Bothrops atrox and Bothrops lanceolatus Venoms In Vitro Investigation: Composition, Procoagulant Effects, Co-Factor Dependency, and Correction Using Antivenoms.Toxins (Basel). 2023 Oct 16;15(10):614. doi: 10.3390/toxins15100614. Toxins (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37888645 Free PMC article.
-
Bothrops venom-induced hemostasis disorders in the rat: Between Scylla and Charybdis.PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2023 Nov 27;17(11):e0011786. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0011786. eCollection 2023 Nov. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2023. PMID: 38011218 Free PMC article.
-
Bothrops (Fer-de-lance) snakebites in the French departments of the Americas (Martinique and Guyana): Clinical and experimental studies and treatment by immunotherapy.PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2023 Feb 28;17(2):e0011083. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0011083. eCollection 2023 Feb. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2023. PMID: 36854042 Free PMC article. Review.
-
New records of helminth infections in Bothrops atrox Linnaeus, 1758 from Marajó Island-Brazil and a literature review with a check list of helminths infecting Bothrops species (Squamata, Viperidae) in the neotropical region.Vet Parasitol Reg Stud Reports. 2024 Aug;53:101060. doi: 10.1016/j.vprsr.2024.101060. Epub 2024 Jun 7. Vet Parasitol Reg Stud Reports. 2024. PMID: 39025553 Review.
Cited by
-
A murine experimental model of the pulmonary thrombotic effect induced by the venom of the snake Bothrops lanceolatus.PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2024 Oct 2;18(10):e0012335. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0012335. eCollection 2024 Oct. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2024. PMID: 39356725 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Resiere D., Kallel H., Florentin J., Houcke S., Mehdaoui H., Gutiérrez J.M., Neviere R. Bothrops (Fer-de-lance) snakebites in the French departments of the Americas (Martinique and Guyana): Clinical and experimental studies and treatment by immunotherapy. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2023;17:e0011083. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0011083. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

