Isolation and Pharmacological Characterisation of Pre-Synaptic Neurotoxins from Thai and Javanese Russell's Viper (Daboia siamensis) Venoms
- PMID: 39330863
- PMCID: PMC11436103
- DOI: 10.3390/toxins16090405
Isolation and Pharmacological Characterisation of Pre-Synaptic Neurotoxins from Thai and Javanese Russell's Viper (Daboia siamensis) Venoms
Abstract
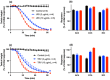
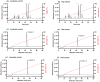
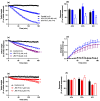
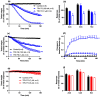
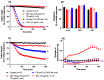
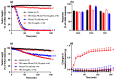
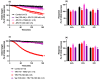
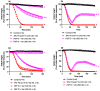
The widespread geographical distribution of Russell's vipers (Daboia spp.) is associated with marked variations in the clinical outcomes of envenoming by species from different countries. This is likely to be due to differences in the quantity and potency of key toxins and, potentially, the presence or absence of some toxins in venoms across the geographical spectrum. In this study, we aimed to isolate and pharmacologically characterise the major neurotoxic components of D. siamensis venoms from Thailand and Java (Indonesia) and explore the efficacy of antivenom and a PLA2 inhibitor, Varespladib, against the neuromuscular activity. These data will provide insights into the link between venom components and likely clinical outcomes, as well as potential treatment strategies. Venoms were fractionated using RP-HPLC and the in vitro activity of isolated toxins assessed using the chick biventer cervicis nerve-muscle preparation. Two major PLA2 fractions (i.e., fractions 8 and 10) were isolated from each venom. Fraction 8 from both venoms produced pre-synaptic neurotoxicity and myotoxicity, whereas fraction 10 from both venoms was weakly neurotoxic. The removal of the two fractions from each venom abolished the in vitro neurotoxicity, and partially abolished myotoxicity, of the whole venom. A combination of the two fractions from each venom produced neurotoxic activity that was equivalent to the respective whole venom (10 µg/mL), but the myotoxic effects were not additive. The in vitro neurotoxicity of fraction 8 (100 nM) from each venom was prevented by the pre-administration of Thai Russell's viper monovalent antivenom (2× recommended concentration) or preincubation with Varespladib (100 nM). Additionally, the neurotoxicity produced by a combination of the two fractions was partially reversed by the addition of Varespladib (100-300 nM) 60 min after the fractions. The present study demonstrates that the in vitro skeletal muscle effects of Thai and Javanese D. siamensis venoms are primarily due to key PLA2 toxins in each venom.
Keywords: Russell’s viper; neuromuscular junction; neurotoxin; phospholipase A2; snake venom.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Gopalan G., Thwin M.M., Gopalakrishnakone P., Swaminathan K. Structural and pharmacological comparison of daboiatoxin from Daboia russelli siamensis with viperotoxin F and vipoxin from other vipers. Acta Crystallogr. D Biol. Crystallogr. 2007;63:722–729. doi: 10.1107/S0907444907016204. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

