Identification of New Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme Inhibitory Peptides Isolated from the Hydrolysate of the Venom of Nemopilema nomurai Jellyfish
- PMID: 39330868
- PMCID: PMC11435582
- DOI: 10.3390/toxins16090410
Identification of New Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme Inhibitory Peptides Isolated from the Hydrolysate of the Venom of Nemopilema nomurai Jellyfish
Abstract
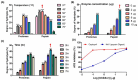
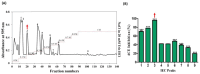
Recently, jellyfish venom has gained attention as a promising reservoir of pharmacologically active compounds, with potential applications in new drug development. In this investigation, novel peptides, isolated from the hydrolysates of Nemopilema nomurai jellyfish venom (NnV), demonstrate potent inhibitory activities against angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE). Proteolytic enzymes-specifically, papain and protamex-were utilized for the hydrolysis under optimized enzymatic conditions, determined by assessing the degree of hydrolysis through the ninhydrin test. Comparative analyses revealed that papain treatment exhibited a notably higher degree of NnV hydrolysis compared to protamex treatment. ACE inhibitory activity was quantified using ACE kit-WST, indicating a substantial inhibitory effect of 76.31% for the papain-digested NnV crude hydrolysate, which was validated by captopril as a positive control. The separation of the NnV-hydrolysate using DEAE sepharose weak-anion-exchange chromatography revealed nine peaks under a 0-1 M NaCl stepwise gradient, with peak no. 3 displaying the highest ACE inhibition of 96%. The further purification of peak no. 3 through ODS-C18 column reverse-phase high-performance liquid chromatography resulted in five sub-peaks (3.1, 3.2, 3.3, 3.4, and 3.5), among which 3.2 exhibited the most significant inhibitory activity of 95.74%. The subsequent analysis of the active peak (3.2) using MALDI-TOF/MS identified two peptides with distinct molecular weights of 896.48 and 1227.651. The peptide sequence determined by MS/MS analysis revealed them as IVGRPLANG and IGDEPRHQYL. The docking studies of the two ACE-inhibitory peptides for ACE molecule demonstrated a binding affinity of -51.4 ± 2.5 and -62.3 ± 3.3 using the HADDOCK scoring function.
Keywords: Neophilia nomurai; angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitor; chromatography; papain enzyme hydrolysate; peptide identification.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Characterization of Novel ACE-Inhibitory Peptides from Nemopilema nomurai Jellyfish Venom Hydrolysate: In Vitro and In Silico Approaches.Mar Drugs. 2025 Jun 26;23(7):267. doi: 10.3390/md23070267. Mar Drugs. 2025. PMID: 40710492 Free PMC article.
-
In vitro angiotensin I converting enzyme inhibition by a peptide isolated from Chiropsalmus quadrigatus Haeckel (box jellyfish) venom hydrolysate.Toxicon. 2016 Sep 1;119:77-83. doi: 10.1016/j.toxicon.2016.04.050. Epub 2016 May 7. Toxicon. 2016. PMID: 27163886
-
Preparation and Identification of ACE Inhibitory Peptides from the Marine Macroalga Ulva intestinalis.Mar Drugs. 2019 Mar 19;17(3):179. doi: 10.3390/md17030179. Mar Drugs. 2019. PMID: 30893907 Free PMC article.
-
Purification and characterization of angiotensin I converting enzyme inhibitory peptides from the rotifer, Brachionus rotundiformis.Bioresour Technol. 2009 Nov;100(21):5255-9. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2009.05.057. Epub 2009 Jun 18. Bioresour Technol. 2009. PMID: 19540110
-
Affinity Purification of Angiotensin Converting Enzyme Inhibitory Peptides from Wakame (Undaria Pinnatifida) Using Immobilized ACE on Magnetic Metal Organic Frameworks.Mar Drugs. 2021 Mar 23;19(3):177. doi: 10.3390/md19030177. Mar Drugs. 2021. PMID: 33807119 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Characterization of Novel ACE-Inhibitory Peptides from Nemopilema nomurai Jellyfish Venom Hydrolysate: In Vitro and In Silico Approaches.Mar Drugs. 2025 Jun 26;23(7):267. doi: 10.3390/md23070267. Mar Drugs. 2025. PMID: 40710492 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bordon K.D.C.F., Cologna C.T., Fornari-Baldo E.C., Pinheiro-Júnior E.L., Cerni F.A., Amorim F.G., Anjolette F.A.P., Cordeiro F.A., Wiezel G.A., Cardoso I.A., et al. From animal poisons and venoms to medicines: Achievements, challenges and perspectives in drug discovery. Front. Pharmacol. 2020;11:1132. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2020.01132. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

