Diagnosis and Management of Neonatal Bacterial Sepsis: Current Challenges and Future Perspectives
- PMID: 39330888
- PMCID: PMC11435811
- DOI: 10.3390/tropicalmed9090199
Diagnosis and Management of Neonatal Bacterial Sepsis: Current Challenges and Future Perspectives
Abstract
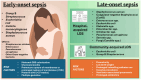
Sepsis remains the second cause of death among neonates after the pathological consequences of extreme prematurity. In this review we summarized knowledge about pathogens causing early-onset sepsis (EOS) and late-onset sepsis (LOS), the role of perinatal risk factors in determining the EOS risk, and the tools used to reduce unnecessary antibiotics. New molecular assays could improve the accuracy of standard blood cultures, providing the opportunity for a quick and sensitive tool. Different sepsis criteria and biomarkers are available to date, but further research is needed to guide the use of antibiotics according to these tools. Beyond the historical antibiotic regimens in EOS and LOS episodes, antibiotics should be based on the local flora and promptly modulated if specific pathogens are identified. The possibility of an antibiotic lock therapy for central venous catheters should be further investigated. In the near future, artificial intelligence could help us to personalize treatments and reduce the increasing trend of multidrug-resistant bacteria.
Keywords: PCR assays; antibiotic lock therapy; biomarkers; blood culture; c-reactive protein; early-onset sepsis; late-onset sepsis; presepsin; procalcitonin; sepsis calculator.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Weiss S.L., Fitzgerald J.C., Pappachan J., Wheeler D., Jaramillo-Bustamante J.C., Salloo A., Singhi S.C., Erickson S., Roy J.A., Bush J.L., et al. Global Epidemiology of Pediatric Severe Sepsis: The Sepsis Prevalence, Outcomes, and Therapies Study. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2015;191:1147–1157. doi: 10.1164/rccm.201412-2323OC. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials