Multidrug-Resistant Proteus mirabilis and Other Gram-Negative Species Isolated from Native Egyptian Chicken Carcasses
- PMID: 39330906
- PMCID: PMC11436119
- DOI: 10.3390/tropicalmed9090217
Multidrug-Resistant Proteus mirabilis and Other Gram-Negative Species Isolated from Native Egyptian Chicken Carcasses
Abstract
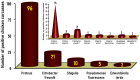
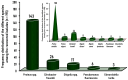
Poultry carcasses may be reservoirs for the zoonotic transmission of antimicrobial-resistant bacteria to humans and pose a major public health hazard. During the isolation of Salmonella from poultry and other foods, many of the presumptive typical Salmonella colonies on xylose lysine deoxycholate (XLD) agar were found to lack the invA gene, which is the specific target gene for Salmonella spp. Therefore, the current study aimed to estimate the prevalence and antimicrobial resistance profiles of extensively drug-resistant invA-negative non-Salmonella isolates recovered from native Egyptian chicken carcasses as presumptive Salmonella colonies on XLD agar. The non-Salmonella isolates were detected in 84% (126/150) of the examined native Egyptian chicken carcasses and classified into five genera, with prevalence rates of 64% (96/150), 14% (21/150), 6.7% (10/150), 3.3% (5/150), and 1.3% (2/150) for Proteus, Citrobacter, Shigella, Pseudomonas, and Edwardsiella, respectively. One hundred and ninety-five invA-negative, non-verified presumptive Salmonella isolates were recovered and classified at the species level into Proteus mirabilis (132/195; 67.7%), Proteus vulgaris (11/195; 5.6%), Citrobacter freundii (26/195; 13.3%), Shigella flexneri (8/195; 4.1%), Shigella sonnei (6/195; 3.1%), Shigella dysenteriae (3/195; 1.5%), Pseudomonas fluorescens (6/195; 3.1%), and Edwardsiella tarda (3/195; 1.5%). All (195/195; 100%) of these isolates showed resistance against cefaclor and fosfomycin. Additionally, these isolates showed high resistance rates of 98%, 92.8%, 89.7%, 89.2%, 89.2%, 86.7%, 80%, 78.5%, 74.4%, and 73.9% against cephalothin, azithromycin, vancomycin, nalidixic acid, tetracycline, sulfamethoxazole/trimethoprim, cefepime, gentamicin, cefotaxime, and ciprofloxacin, respectively. Interestingly, all (195/195; 100%) of the identified isolates were resistant to at least five antibiotics and exhibited an average MAR (multiple antibiotic resistance) index of 0.783. Furthermore, 73.9% of the examined isolates were classified as extensively drug-resistant, with an MAR index equal to 0.830. The high prevalence of extensively drug-resistant foodborne Proteus, Citrobacter, Shigella, Pseudomonas, and Edwardsiella isolated from native chicken carcasses poses a great hazard to public health and necessitates more monitoring and concern about the overuse and misuse of antibiotics in humans and animals. This study also recommends the strict implementation of GHP (good hygienic practices) and GMP (good manufacturing practices) in the chicken meat supply chain to protect consumer health.
Keywords: Proteus vulgaris; Proteus mirabilis; Shigella; chicken meat; multidrug-resistant.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Colistin-, cefepime-, and levofloxacin-resistant Salmonella enterica serovars isolated from Egyptian chicken carcasses.Ann Clin Microbiol Antimicrob. 2024 Jul 4;23(1):61. doi: 10.1186/s12941-024-00713-3. Ann Clin Microbiol Antimicrob. 2024. PMID: 38965586 Free PMC article.
-
Extensively drug-, ciprofloxacin-, cefotaxime-, and azithromycin-resistant Salmonella enterica serovars isolated from camel meat in Egypt.Int J Food Microbiol. 2024 Feb 2;411:110538. doi: 10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2023.110538. Epub 2023 Dec 20. Int J Food Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 38134580
-
Susceptibility antibiotic screening reveals high rates of multidrug resistance of Salmonella, Shigella and Campylobacter in HIV infected and uninfected patients from Mozambique.BMC Infect Dis. 2023 Apr 21;23(1):255. doi: 10.1186/s12879-023-08219-7. BMC Infect Dis. 2023. PMID: 37085752 Free PMC article.
-
Prevalence and antimicrobial resistance profile of bacterial foodborne pathogens in Nile tilapia fish (Oreochromis niloticus) at points of retail sale in Nairobi, Kenya.Front Antibiot. 2023 May 24;2:1156258. doi: 10.3389/frabi.2023.1156258. eCollection 2023. Front Antibiot. 2023. PMID: 39816642 Free PMC article.
-
Antimicrobial resistance and resistance genes in Salmonella strains isolated from broiler chickens along the slaughtering process in China.Int J Food Microbiol. 2017 Oct 16;259:43-51. doi: 10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2017.07.023. Epub 2017 Aug 1. Int J Food Microbiol. 2017. PMID: 28800411
Cited by
-
Antibiotic-Resistant Shigella sonnei Bacteremia in an Immunocompetent Postgastric Bypass Patient Without Typical Risk Factors.Case Rep Infect Dis. 2025 Mar 27;2025:9910105. doi: 10.1155/crdi/9910105. eCollection 2025. Case Rep Infect Dis. 2025. PMID: 40182068 Free PMC article.
-
Antibiotic resistance gene pollution in poultry farming environments and approaches for mitigation: A system review.Poult Sci. 2025 Mar;104(3):104858. doi: 10.1016/j.psj.2025.104858. Epub 2025 Jan 25. Poult Sci. 2025. PMID: 39874786 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Parija S.C. Textbook of Microbiology and Immunology. Springer Nature; Singapore: 2023. - DOI
-
- Galal S. Annual Chicken Meat Production in Egypt 2010–2023. [(accessed on 6 September 2024)]. Available online: https://www.statista.com/statistics/1005988/egypt-chicken-meat-productio....
-
- Adzitey F., Huda N., Gulam R. Comparison of media for the isolation of Salmonella (XLD and Rambach) and Listeria species (ALOA and Palcam) in naturally contaminated duck samples. Internet J. Food Saf. 2011;13:20–25.
-
- Sun Y., Wen S., Zhao L., Xia Q., Pan Y., Liu H., Wei C., Chen H., Ge J., Wang H. Association among Biofilm Formation, virulence gene expression, and antibiotic resistance in Proteus mirabilis isolates from diarrhetic animals in Northeast China. BMC Vet. Res. 2020;16:176. doi: 10.1186/s12917-020-02372-w. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

