Hypoxia-inducible factor-2α enhances neutrophil survival to promote cardiac injury following myocardial infarction
- PMID: 39331023
- PMCID: PMC11559636
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpheart.00392.2024
Hypoxia-inducible factor-2α enhances neutrophil survival to promote cardiac injury following myocardial infarction
Abstract
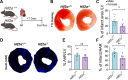
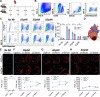
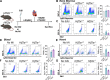
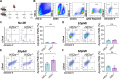
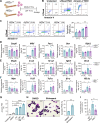
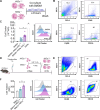
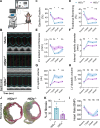
Heart failure is a major cause of mortality following myocardial infarction. Neutrophils are among the first immune cells to accumulate in the infarcted region. Although beneficial functions of neutrophils in heart injury are now appreciated, neutrophils are also well known for their ability to exacerbate inflammation and promote tissue damage. Myocardial infarction induces hypoxia, where hypoxia-inducible factors (HIFs) are activated and play critical roles in cellular functions. In this context, the role of Hif2α in neutrophils during myocardial infarction is unknown. Here, we demonstrate that neutrophil Hif2α deletion markedly attenuates myocardial infarct size, improves cardiac function, reduces neutrophil survival and tissue accumulation, and correlates with increased macrophage engulfment rates. Mechanistic studies revealed that Hif2α promotes neutrophil survival through binding to hypoxia response element (HRE) in the promoter region of Birc2 to regulate expression of the prosurvival factor, cellular inhibitor of apoptosis protein-1 (cIAP1). Inhibition of cIAP1 in neutrophils using the pharmacological agent, Birinapant resulted in increased cell death, establishing a critical role of cIAP1 downstream of Hif2α in neutrophil survival. Taken together, our data demonstrate a protective effect of Hif2α deletion in neutrophils on cardiac injury outcomes through modulation of neutrophil cell survival.NEW & NOTEWORTHY Hif2α in neutrophils increases infarct size, cardiac dysfunction, and ventricular scar after myocardial infarction. Hif2α in neutrophils supports neutrophil survival via cIAP-1 signaling and delays macrophage engulfment.
Keywords: Hif2α; apoptosis; inflammation; myocardial infarction; neutrophil.
Conflict of interest statement
No conflicts of interest, financial or otherwise, are declared by the authors.
Figures
Comment in
-
Hypoxic neutrophils enflame the infarcted heart.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2024 Nov 1;327(5):H1303-H1305. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00701.2024. Epub 2024 Oct 25. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2024. PMID: 39453434 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Jung SH, Hwang BH, Shin S, Park EH, Park SH, Kim CW, Kim E, Choo E, Choi IJ, Swirski FK, Chang K, Chung YJ. Spatiotemporal dynamics of macrophage heterogeneity and a potential function of Trem2hi macrophages in infarcted hearts. Nat Commun 13: 4580, 2022. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-32284-2. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

