Ternary TiO2/MoS2/ZnO hetero-nanostructure based multifunctional sensing devices
- PMID: 39331285
- PMCID: PMC11436549
- DOI: 10.1186/s11671-024-04112-7
Ternary TiO2/MoS2/ZnO hetero-nanostructure based multifunctional sensing devices
Abstract
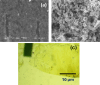
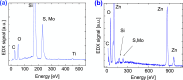
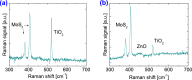
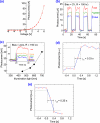
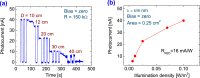
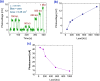
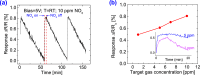
Novel sensing applications benefit from multifunctional nanomaterials responsive to various external stimuli such as mechanics, electricity, light, humidity, or pollution. While few such materials occur naturally, the careful design of synergized nanomaterials unifies the cross-coupled properties which are weak or absent in single-phase materials. In this study, 2D MoS2 integrated with ultrathin dielectric oxide layers forms hetero-nanostructures with significant impacts on carrier transport. The ternary TiO2/MoS2/ZnO hetero-nanostructures, along with their individual properties, improve the performance of multifunctional sensing devices. The synthesized hetero-nanostructure exhibits a responsivity of up to 16 mA/W to 700 nm light and responds to 5 ppm ammonia gas at room temperature. These enhancements are attributed to interface charge transfer and photogating effects. The ternary TiO2/MoS2/ZnO hetero-nanostructure is compatible with existing semiconductor fabrication technologies, making it feasible to integrate into flexible, lightweight semiconductor devices and circuits. These results may inspire new photodetectors and sensing devices based on two-dimensional (2D) layered materials for IoT applications.
Keywords: Gas sensor; Molybdenum disulfide; Multifunctional sensor; Photodetector; Ternary hetero-nanostructure; Titanium dioxide; Two-dimensional material; Zinc oxide.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Wang J, Lim MK, Wang C, Tseng ML. The evolution of the Internet of Things (IoT) over the past 20 years. Comput Ind Eng. 2021;155:107174.
-
- Jamshed MA, Ali K, Abbasi QH, Imran MA, Ur-Rehman M. Challenges, applications, and future of wireless sensors in Internet of Things: a review. IEEE Sens J. 2022;22(6):5482–94.
-
- Aslam A, Mehmood U, Arshad MH, Ishfaq A, Zaheer J, Khan AUH, Sufyan M. Dye-sensitized solar cells (DSSCs) as a potential photovoltaic technology for the self-powered internet of things (IoTs) applications. Sol Energy. 2020;207:874–92.
-
- Yang Y, Guo X, Zhu M, Sun Z, Zhang Z, He T, Lee C. Triboelectric nanogenerator enabled wearable sensors and electronics for sustainable internet of things integrated green earth. Adv Energy Mater. 2023;13(1):2203040.
-
- Portilla L, Loganathan K, Faber H, Eid A, Hester JG, Tentzeris MM, Fattori M, Cantatore E, Jiang C, Nathan A, Fiori G. Wirelessly powered large-area electronics for the Internet of Things. Nat Electronics. 2023;6(1):10–7.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
