Multiomic biomarkers after cardiac arrest
- PMID: 39331333
- PMCID: PMC11436561
- DOI: 10.1186/s40635-024-00675-y
Multiomic biomarkers after cardiac arrest
Abstract
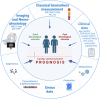
Cardiac arrest is a sudden cessation of heart function, leading to an abrupt loss of blood flow and oxygen to vital organs. This life-threatening emergency requires immediate medical intervention and can lead to severe neurological injury or death. Methods and biomarkers to predict neurological outcome are available but lack accuracy. Such methods would allow personalizing healthcare and help clinical decisions. Extensive research has been conducted to identify prognostic omic biomarkers of cardiac arrest. With the emergence of technologies allowing to combine different levels of omics data, and with the help of artificial intelligence and machine learning, there is a potential to use multiomic signatures as prognostic biomarkers after cardiac arrest. This review article delves into the current knowledge of cardiac arrest biomarkers across various omic fields and suggests directions for future research aiming to integrate multiple omics data layers to improve outcome prediction and cardiac arrest patient's care.
Keywords: Artificial intelligence; Biomarkers; Cardiac arrest; Clinical outcomes; Machine learning; Multiomics; Prognosis.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Y.D. holds patents and licensing agreements related to the use of RNAs for diagnostic and therapeutic purposes, and is member of the Scientific Advisory Board of Firalis SA. Other authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Streitberger KJ, Leithner C, Wattenberg M, Tonner PH, Hasslacher J, Joannidis M, Pellis T, Di Luca E, Födisch M, Krannich A, Ploner CJ (2017) Neuron-specific enolase predicts poor outcome after cardiac arrest and targeted temperature management: a multicenter study on 1,053 patients. Critical Care Med 45(7):1145–1151 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Cummins RO, Ornato JP, Thies WH, Pepe PE (1991) Improving survival from sudden cardiac arrest: the “chain of survival” concept. A statement for health professionals from the advanced cardiac life support subcommittee and the emergency cardiac care committee. Am Heart Assoc Circ 83:1832–1847 - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

