Liquid Atmospheric Pressure Matrix-Assisted Laser Desorption/Ionization Mass Spectrometry Using a Commercial Ion Source and Orbitrap Mass Analyzer
- PMID: 39331381
- PMCID: PMC11465227
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.analchem.4c04458
Liquid Atmospheric Pressure Matrix-Assisted Laser Desorption/Ionization Mass Spectrometry Using a Commercial Ion Source and Orbitrap Mass Analyzer
Abstract
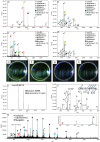
A liquid atmospheric pressure-matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization (LAP-MALDI) method has been developed and applied to a commercial AP-MALDI source on a hybrid orbitrap mass analyzer. It is shown that electrospray ionization (ESI)-like mass spectra of a range of peptides and proteins can be acquired by LAP-MALDI mass spectrometry (MS) as previously demonstrated on a homemade LAP-MALDI-Q-TOF setup but without the need of any modification to the commercially available MS equipment used. Multiply charged peptide ions were recorded with a resolution of around 100,000 and a mass accuracy of less than 5 ppm. The higher resolution and mass accuracy of the orbitrap analyzer compared with previously employed Q-TOF instrumentation provided high confidence in bacterial proteoform and species identification by top-down protein analysis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
A high resolution atmospheric pressure matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization-quadrupole-orbitrap MS platform enables in situ analysis of biomolecules by multi-mode ionization and acquisition.Anal Chim Acta. 2018 May 12;1007:16-25. doi: 10.1016/j.aca.2017.12.045. Epub 2018 Jan 6. Anal Chim Acta. 2018. PMID: 29405984 Free PMC article.
-
Commercial intermediate pressure MALDI ion mobility spectrometry mass spectrometer capable of producing highly charged laserspray ionization ions.Anal Chem. 2011 Feb 1;83(3):678-84. doi: 10.1021/ac102779e. Epub 2010 Dec 17. Anal Chem. 2011. PMID: 21166462
-
Comparison of the effects of ionization mechanism, analyte concentration, and ion "cool-times" on the internal energies of peptide ions produced by electrospray and atmospheric pressure matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization.J Am Soc Mass Spectrom. 2005 May;16(5):743-51. doi: 10.1016/j.jasms.2005.01.018. J Am Soc Mass Spectrom. 2005. PMID: 15862775
-
Hybrid quadrupole/time-of-flight mass spectrometers for analysis of biomolecules.Methods Enzymol. 2005;402:49-78. doi: 10.1016/S0076-6879(05)02002-1. Methods Enzymol. 2005. PMID: 16401506 Review.
-
Direct profiling of tissue lipids by MALDI-TOFMS.J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2009 Sep 15;877(26):2822-9. doi: 10.1016/j.jchromb.2008.11.033. Epub 2008 Nov 28. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2009. PMID: 19095508 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Direct Colony Atmospheric Pressure Matrix-Assisted Laser Desorption/Ionization Mass Spectrometry Assay for Targeted Operon Metabolite Analysis.Methods Mol Biol. 2025;2925:173-184. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-4534-5_12. Methods Mol Biol. 2025. PMID: 40498189
-
Integrating the milk microbiome signatures in mastitis: milk-omics and functional implications.World J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2025 Jan 18;41(2):41. doi: 10.1007/s11274-024-04242-1. World J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2025. PMID: 39826029 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Hale O. J.; Cramer R. Collision-induced dissociation of doubly-charged barium-cationized lipids generated from liquid samples by atmospheric pressure matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization provides structurally diagnostic product ions. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2018, 410, 1435–1444. 10.1007/s00216-017-0788-6. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Krenkel H.; Brown J.; Morris M.; Cramer R. The use of salts, buffers and surfactants in LAP-MALDI MS. Int. J. Mass Spectrom. 2023, 493, 11713410.1016/j.ijms.2023.117134. - DOI
-
- Sampson J. S.; Hawkridge A. M.; Muddiman D. C. Generation and detection of multiply-charged peptides and proteins by matrix-assisted laser desorption electrospray ionization (MALDESI) Fourier transform ion cyclotron resonance mass spectrometry. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 2006, 17, 1712–1716. 10.1016/j.jasms.2006.08.003. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

