Identification of ferroptosis biomarkers and immune infiltration landscapes in atrial fibrillation: A bioinformatics analysis
- PMID: 39331874
- PMCID: PMC11441859
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000039777
Identification of ferroptosis biomarkers and immune infiltration landscapes in atrial fibrillation: A bioinformatics analysis
Abstract
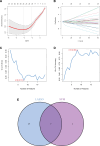
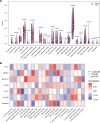
Ferroptosis has been recognized as a critical factor in the development of atrial fibrillation (AF), but its precise mechanisms remain unclear. We downloaded the GSE115574 dataset from the gene expression omnibus database to analyze the expression levels of ferroptosis-related genes (FRGs) and identify differentially expressed genes (DEGs). Least absolute shrinkage and selection operator (LASSO) and support vector machine-recursive feature elimination (SVM-RFE) machine learning techniques were employed to identify key genes associated with AF. The diagnostic performance of these genes was evaluated using Receiver operating characteristic curves (ROC) and validated in an independent AF dataset. miRNA and lncRNA predictions for potential binding to these key genes were conducted using miRBase, miRDB, and TargetScan. Furthermore, gene set enrichment analysis (GSEA) enrichment analysis, immune cell infiltration analysis, and targeted drug prediction were performed. The intersection of LASSO regression and SVM-RFE analyses identified 7 DEGs significantly associated with AF. Validation through ROC and an additional dataset confirmed the importance of MAPK14, CAV1, and ADAM23. Significant infiltration of memory B cells, regulatory T cells, and monocytes was observed in atrial tissues. Seventy-two miRNAs were predicted to potentially target MAPK14, and 2 drugs were identified as targeting CAV1. This study underscores the involvement of FRGs in AF through machine learning and validation approaches. The observed immune cell infiltration suggests a potential link between immune response and AF. The predicted ceRNA network offers new insights into gene regulation, presenting potential biomarkers and therapeutic targets for AF.
Copyright © 2024 the Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no funding and conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures




References
-
- Baman JR, Passman RS. Atrial fibrillation. JAMA. 2021;325:2218. - PubMed
-
- Lee M, Lee BC, Yu KH, et al. CRCS-K Investigators. Secular trends in outcomes and impact of novel oral anticoagulants in atrial fibrillation-related acute ischemic stroke. Stroke. 2024;55:625–33. - PubMed
-
- Lau DH, Linz D, Sanders P. New findings in atrial fibrillation mechanisms. Card Electrophysiol Clin. 2019;11:563–71. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

