Optokinetic response in D. melanogaster reveals the nature of common repellent odorants
- PMID: 39333197
- PMCID: PMC11436819
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-73221-1
Optokinetic response in D. melanogaster reveals the nature of common repellent odorants
Abstract
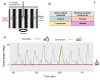
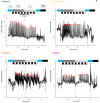
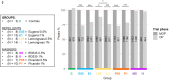
Animals' ability to orient and navigate relies on selecting an appropriate motor response based on the perception and integration of the environmental information. This is the case, for instance, of the optokinetic response (OKR) in Drosophila melanogaster, where optic flow visual stimulation modulates head movements. Despite a large body of literature on the OKR, there is still a limited understanding, in flies, of the impact on OKR of concomitant, and potentially conflicting, inputs. To evaluate the impact of this multimodal integration, we combined in D. melanogaster, while flying in a tethered condition, the optic flow stimulation leading to OKR with the simultaneous presentation of olfactory cues, based on repellent or masking compounds typically used against noxious insect species. First, this approach allowed us to directly quantify the effect of several substances and of their concentration on the dynamics of the flies' OKR in response to moving gratings by evaluating the number of saccades and the velocity of the slow phase. Subsequently, this analysis was capable of easily revealing the actual effect, i.e. masking vs. repellent, of the compound tested. In conclusion, we show that D. melanogaster, a cost-affordable species, represents a viable option for studying the effects of several compounds on the navigational abilities of insects.
Keywords: Drosophila melanogaster; Navigation; Optokinetic response; Repellents.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.Entostudio S.r.l. is not involved in the production nor the distribution of any of the tested compounds and did not receive any funding related to the present article. The work presented in this paper was funded by the PON - DM 1061 PhD scholarship from Italian Ministry for University and Research (MUR) assigned to Menti G. M., the Università degli Sudi di Padova’s DOR funding to Megighian A., and the PRIN 2020 funding from MUR to Megighian A. and dal Maschio M.
Figures


References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

