Magnitude and kinetics of a set of neuroanatomic volume and thickness together with white matter hyperintensity is definitive of cognitive status and brain age
- PMID: 39333492
- PMCID: PMC11437080
- DOI: 10.1038/s41398-024-03097-2
Magnitude and kinetics of a set of neuroanatomic volume and thickness together with white matter hyperintensity is definitive of cognitive status and brain age
Abstract
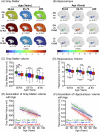
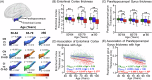
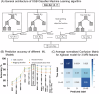
Even among the subjects classified as cognitively normal, there exists a subset of individuals at a given chronological age (CA) who harbor white matter hyperintensity (WMH) while another subset presents with low or undetectable WMH. Here, we conducted a comprehensive MRI segmentation of neuroanatomic structures along with WMH quantification in groups of cognitively normal (CN), cognitively impaired (CI) individuals, and individuals with an etiological diagnosis of cognitive impairment owing to Alzheimer's Disease (CI-AD) across the early (50-64 years), intermediate (65-79 years), and late (≥80 years) age groups from the NACC cohort. Neuroanatomic volumetry quantification revealed that thinning of the parahippocampal gyrus in the early (p = 0.016) and intermediate age groups (p = 0.0001) along with an increase in CSF (p = 0.0009) delineates between CI and CI-AD subjects. Although, a significant loss of ~5-10% in volume of gray matter (p(CN vs CI) < 0.0001, p(CN vs CI-AD) < 0.0001), white matter (p(CN vs CI) = 0.002, p(CN vs CI-AD) = 0.0003) and hippocampus (p(CN vs CI) = 0.007, p(CN vs CI-AD) < 0.0001) was evident at the early age groups in the CI and CI-AD compared to CN but it was not distinct between CI and CI-AD. Using the neuroanatomic and WMH volume, and the supervised decision tree-based ML modeling, we have established that a minimum set of Three brain quantities; Total brain (GM + WM), CSF, and WMH volume, provide the Optimal quantitative features discriminative of cognitive status as CN, CI, and CI-AD. Furthermore, using the volume/thickness of 178 neuroanatomic structures, periventricular and deep WMH volume quantification for the 819 CN subjects, we have developed a quantitative index as 'Brain Age' (BA) depictive of neuroanatomic health at a given CA. Subjects with elevated WMH load (5-10 ml) had increased BA ( + 0.6 to +4 years) than the CA. Increased BA in the subjects with elevated WMH is suggestive of WMH-induced vascular insult leading to accelerated and early structural loss than expected for a given CA. Henceforth, this study establishes that quantification of WMH together with an optimal number of neuroanatomic features is mandatory to delve into the biological underpinning of aging and aging-associated cognitive disorders.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- U24 AG072122/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG062429/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG066468/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG062421/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG066509/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG066514/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG066530/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG066507/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG066444/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG066518/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG066512/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG066462/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG072979/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG072972/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG072976/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG072975/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG072978/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG072977/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG066519/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG062677/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG079280/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG062422/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG066511/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG072946/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG062715/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG072973/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG066506/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG066508/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG066515/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG072947/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG072931/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG066546/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P20 AG068024/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P20 AG068053/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P20 AG068077/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P20 AG068082/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG072958/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG072959/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AG024904/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

