A novel bacterial effector protein mediates ER-LD membrane contacts to regulate host lipid droplets
- PMID: 39333627
- PMCID: PMC11624262
- DOI: 10.1038/s44319-024-00266-8
A novel bacterial effector protein mediates ER-LD membrane contacts to regulate host lipid droplets
Abstract
Effective intracellular communication between cellular organelles occurs at dedicated membrane contact sites (MCSs). Tether proteins are responsible for the establishment of MCSs, enabling direct communication between organelles to ensure organelle function and host cell homeostasis. While recent research has identified tether proteins in several bacterial pathogens, their functions have predominantly been associated with mediating inter-organelle communication between the bacteria containing vacuole (BCV) and the host endoplasmic reticulum (ER). Here, we identify a novel bacterial effector protein, CbEPF1, which acts as a molecular tether beyond the confines of the BCV and facilitates interactions between host cell organelles. Coxiella burnetii, an obligate intracellular bacterial pathogen, encodes the FFAT motif-containing protein CbEPF1 which localizes to host lipid droplets (LDs). CbEPF1 establishes inter-organelle contact sites between host LDs and the ER through its interactions with VAP family proteins. Intriguingly, CbEPF1 modulates growth of host LDs in a FFAT motif-dependent manner. These findings highlight the potential for bacterial effector proteins to impact host cellular homeostasis by manipulating inter-organelle communication beyond conventional BCVs.
Keywords: Coxiella burnetii; FFAT Motif; Inter-organelle Contacts; Lipid Droplets; Molecular Tethers.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure and competing interests statement. The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



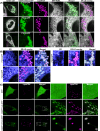
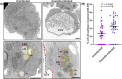





Update of
-
The novel bacterial effector protein CbEPF1 mediates ER-LD membrane contacts to regulate host lipid droplet metabolism.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2023 Dec 11:2023.12.11.571031. doi: 10.1101/2023.12.11.571031. bioRxiv. 2023. Update in: EMBO Rep. 2024 Dec;25(12):5331-5351. doi: 10.1038/s44319-024-00266-8. PMID: 38168204 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
-
- Alpy F, Rousseau A, Schwab Y, Legueux F, Stoll I, Wendling C, Spiegelhalter C, Kessler P, Mathelin C, Rio M-C et al (2013) STARD3 or STARD3NL and VAP form a novel molecular tether between late endosomes and the ER. J Cell Sci 126:5500–5512 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

