Natriuretic peptides and soluble ST2 improves echocardiographic diagnosis of elevated left ventricular filling pressures
- PMID: 39333652
- PMCID: PMC11436802
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-73349-0
Natriuretic peptides and soluble ST2 improves echocardiographic diagnosis of elevated left ventricular filling pressures
Abstract
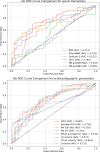
Elevated filling pressure of the left ventricle (LV) defines diastolic dysfunction. The gold standard for diagnosis is represented by the measurement of LV end-diastolic pressure (LVEDP) during cardiac catheterization, but it has the disadvantage of being an invasive procedure. This study aimed to investigate the correlation between LVEDP and cardiac serum biomarkers such as natriuretic peptides (mid-regional pro-atrial natriuretic peptide [MR-proANP], B-type natriuretic peptide [BNP], and N-terminal prohormone BNP [NT-proBNP]), soluble ST2 (sST2), galectin-3 and mid-regional pro-adrenomedullin (MR-proAMD). Consecutive patients hospitalized in a tertiary center and undergoing left cardiac catheterization were included in the study. Diastolic dysfunction was considered present if the end-expiratory LVEDP was ≥ 15 mmHg. Cardiac biomarkers were determined from pre-procedural peripheral venous blood samples. A total of 110 patients were included, of whom 76 (69.0%) were males, with a median age of 65 (55-71) years. Median LVEDP was 13.5 (8-19) mmHg and diastolic dysfunction was present in 50 (45.4%) of the patients. LVEDP correlated with BNP (p < 0.0001, r = 0.39 [0.20-0.53]), NT-proBNP (p < 0.0001, r = 0.40 [0.22-0.55]), MR-proANP (p = 0.001, r = 0.30 [0.11-0.46]), sST2 (p < 0.0001, r = 0.47 [0.30-0.60]), but not with MR-proAMD (p = 0.77) or galectin-3 (p = 0.76). In the final stepwise multivariable binary logistic regression model, diastolic dysfunction was predicted by NT-proBNP, mitral average E/e', sST2, atrial fibrillation, and left atrium reservoir strain. BNP, NT-proBNP, MR-proANP, and sST2 had predictive value for diastolic dysfunction. In contrast, galectin-3 and MR-proAMD were not associated with increased filling pressures. Furthermore, NT-proBNP and sST2 significantly improved diastolic dysfunction prediction in the final multivariable model.
Keywords: B-type natriuretic peptide; Diastolic dysfunction; Galectin-3; Mid-regional pro-adrenomedullin.; Mid-regional pro-atrial natriuretic peptide; N-terminal prohormone B-type natriuretic peptide; Soluble ST2.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- McDonagh, T. A. et al. ESC Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure: Developed by the Task Force for the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) With the special contribution of the Heart Failure Association (HFA) of the ESC. European Heart J. 42, 3599–3726 (2021). (2021).
-
- Galderisi, M. et al. European multicentre validation study of the accuracy of E/e′ ratio in estimating invasive left ventricular filling pressure: EURO-FILLING study. Eur. Heart J. - Cardiovasc. Imaging. 15, 810–816 (2014). - PubMed
-
- Lancellotti, P. et al. Echo-Doppler estimation of left ventricular filling pressure: results of the multicentre EACVI Euro-Filling study. Eur. Heart J. - Cardiovasc. Imaging. 18, 961–968 (2017). - PubMed
-
- Nauta, J. F. et al. Correlation with invasive left ventricular filling pressures and prognostic relevance of the echocardiographic diastolic parameters used in the 2016 ESC heart failure guidelines and in the 2016 ASE/EACVI recommendations: a systematic review in patients with heart failure with preserved ejection fraction. Eur. J. Heart Fail.20, 1303–1311 (2018). - PubMed
-
- Sharifov, O. F., Schiros, C. G., Aban, I., Denney, T. S. & Gupta, H. Diagnostic accuracy of tissue Doppler Index E/e’ for evaluating left ventricular filling pressure and diastolic Dysfunction/Heart failure with preserved ejection fraction: a systematic review and Meta-analysis. J. Am. Heart Assoc.5, e002530 (2016). - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

