Evaluation of risk for bronchiolitis obliterans syndrome after allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation with myeloablative conditioning regimens
- PMID: 39333758
- PMCID: PMC11611741
- DOI: 10.1038/s41409-024-02422-z
Evaluation of risk for bronchiolitis obliterans syndrome after allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation with myeloablative conditioning regimens
Abstract
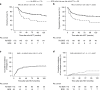
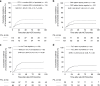
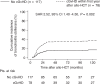
Bronchiolitis obliterans syndrome (BOS), as chronic manifestation of graft-versus-host disease (GVHD), is a debilitating complication leading to lung function deterioration in patients after allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation (allo-HCT). In the present study, we evaluated BOS development risk in patients after receiving myeloablative conditioning (MAC) regimens. We performed a retrospective analysis of patients undergoing allo-HCT, who received MAC with busulfan/cyclophosphamid (BuCy, n = 175) busulfan/fludarabin (FluBu4, n = 29) or thiotepa/busulfan/fludarabine (TBF MAC, n = 37). The prevalence of lung disease prior allo-HCT, smoking status, GvHD prophylaxis, HCT-CI score, EBMT risk score and GvHD incidence varied across the groups. The cumulative incidence of BOS using the NIH diagnosis consensus criteria at 2 years after allo-HCT was 8% in FluBu4, 23% in BuCy and 19% in TBF MAC (p = 0.07). In the multivariate analysis, we identified associated factors for time to BOS such as FEV1<median (99% of predicted) (HR = 2.39, p = 0.004), CMV patient serology positivity (HR = 2.11, p = 0.014), TLC < 80% of predicted (HR = 0.12, p = 0.02) and GvHD prophylaxis with in vivo T-cell depletion (HR = 0.29, p = 0.001) as predictors of BOS. In summary, we identified risk factors for BOS development in patients receiving MAC conditioning. These findings might serve to identify patients at risk, who might benefit from closely monitoring or early therapeutic interventions.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no conflicting financial interest with the submission of this article. JF received research support and speakers honoraria from Medac, Neovii and Riemser. JD-A received speaker’s honoraria from Roche, Amgen, AstraZeneca, Riemser, Sobi, Lilly, Beigene and Ipsen and travel support from Gilead, Sobi, Beigene, Alexion and Abbvie. RZ received speaker’s honoraria from Incyte, Novartis, Roche and Mallinckroth. D Stolz reports personal fees from CSL Behring, Berlin-Chemie Menarini, Novartis, GlaxoSmithKline, AstraZeneca, Vifor, Merck, Chiesi, Grifols, MSD, Merck, Sanofi, Roche, Boehringer-Ingelheim and Pfizer, and participation on advisory boards for CSL Behring, Berlin-Chemie, Menarini, Novartis, Boehringer-Ingelheim, GlaxoSmithKline, AstraZeneca, Vifor, Merck, Chiesi, Roche, Grifols, MSD, Merck and Sanofi. This project was supported by a grant of the German Federal Ministry of Education and Research (BMBF 01 EO 0803). JD-A received support from Else Kröner-Fresenius-Stiftung (Nr. 2018-A56). JD-A received research support from German Research Foundation (Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft, ref. DU 1287/3-1 and 1287/5-1), from the Forschungskommission of the University of Freiburg Medical School (DUQ1106/16) and Berta Ottenstein-Programm for Advanced Clinician Scientists, Faculty of Medicine, University of Freiburg. KM-B received support from Else-Kröner-Fresenius-Stiftung (2021_EKEA.131), the Berta-Ottenstein Program (Faculty of Medicine, Freiburg University), and the IMMediate Advanced Clinician Scientist-Program, Department of Medicine II, Medical Center – University of Freiburg and Faculty of Medicine, University of Freiburg, funded by the Bundesministerium für Bildung und Forschung (BMBF, Federal Ministry of Education and Research) - 01EO2103.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

