Predictive value of platelet-to-albumin ratio combined with the C2HEST score for New-Onset atrial fibrillation in elderly patients with acute ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction
- PMID: 39333846
- PMCID: PMC11429877
- DOI: 10.1186/s12872-024-04200-7
Predictive value of platelet-to-albumin ratio combined with the C2HEST score for New-Onset atrial fibrillation in elderly patients with acute ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction
Abstract
Background: New-onset atrial fibrillation (NOAF) is a common adverse outcome in acute ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI) patients following percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) and is associated with a worse prognosis. The platelet-to-albumin ratio (PAR) has been utilized to predict the severity and prognosis of cardiovascular diseases. This study aims to investigate the predictive value of PAR combined with the C2HEST score for NOAF in the elderly population with STEMI undergoing PCI.
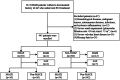
Methods: 445 elderly STEMI patients without a history of atrial fibrillation (AF) who underwent PCI were consecutively enrolled in this study. Multivariate logistic regression analysis was used to identify independent risk factors for NOAF after PCI.
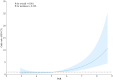
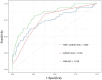
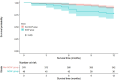
Results: 50 patients (11.2%) developed NOAF after PCI. Multivariate logistic regression analysis revealed that heart rate (HR), systemic immune-inflammation index (SII), uric acid (UA), PAR, and C2HEST score were independent risk factors for NOAF. The area under the curve (AUC) of the combined PAR and C2HEST score was 0.839, and Delong's test indicated that the combined model had superior predictive value compared to individual markers (AUC of PAR: 0.738; AUC of C2HEST score: 0.752) (P < 0.05). The addition of PAR and C2HEST score to this model (HR, SII, and UA) significantly improved the reclassification and discrimination ability (IDI 0.175; NRI 0.734, both P < 0.001). During regular follow-up, the incidence of MACE was higher in the NOAF group compared to the non-NOAF group.
Conclusion: The combination of PAR and the C2HEST score has a high predictive value for NOAF in elderly STEMI patients following PCI.
Keywords: Acute myocardial infarction; C2HEST score; Elderly; New-onset atrial fibrillation; Platelet to albumin ratio.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Mazzone A, Scalese M, Paradossi U, Del Turco S, Botto N, De Caterina A, Trianni G, Ravani M, Rizza A, Molinaro S, et al. Development and validation of a risk stratification score for new-onset atrial fibrillation in STEMI patients undergoing primary percutaneous coronary intervention. Int J Clin Pract. 2018;72(4):e13087. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Rene AG, Généreux P, Ezekowitz M, Kirtane AJ, Xu K, Mehran R, Brener SJ, Stone GW. Impact of atrial fibrillation in patients with ST-elevation myocardial infarction treated with percutaneous coronary intervention (from the HORIZONS-AMI [Harmonizing outcomes with revascularization and stents in Acute Myocardial Infarction] trial). Am J Cardiol. 2014;113(2):236–42. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Morishima I, Tomomatsu T, Okumura K, Sone T, Tsuboi H, Morita Y, Inoue Y, Yoshida R, Yura Y, Murohara T. New-onset atrial fibrillation may be a more important predictor of cardiac mortality in acute myocardial infarction patients than preexisting atrial fibrillation. Int J Cardiol. 2015;187:475–7. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Petersen JK, Butt JH, Yafasova A, Torp-Pedersen C, Sørensen R, Kruuse C, Vinding NE, Gundlund A, Køber L, Fosbøl EL, Østergaard L. Incidence of ischaemic stroke and mortality in patients with acute coronary syndrome and first-time detected atrial fibrillation: a nationwide study. Eur Heart J. 2021;42(44):4553–61. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous