First real-world study on the effectiveness and tolerability of rimegepant for acute migraine therapy in Chinese patients
- PMID: 39333875
- PMCID: PMC11438109
- DOI: 10.1186/s10194-024-01873-5
First real-world study on the effectiveness and tolerability of rimegepant for acute migraine therapy in Chinese patients
Abstract
Background: Rimegepant, a small molecule calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) receptor antagonist, is indicated for acute and preventive migraine treatment in the United States and other countries. However, there is a lack of prospective real-world evidence for the use of rimegepant in Chinese migraine patients.
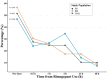
Methods: This was a single-arm, prospective, real-world study. While taking rimegepant to treat migraine attacks as needed, eligible participants were asked to record their pain intensity, functional ability, and accompanying symptoms for a single attack at predose and 0.5, 1, 2, 24, and 48 h postdose via a digital platform. Adverse events (AEs) during the rimegepant treatment period were recorded and analysed. The percentages of participants who experienced moderate to severe pain at predose and 0.5, 1, 2, 24, and 48 h postdose were assessed. Additionally, the percentages of participants who reported better/good outcomes in terms of pain intensity, functional ability, and accompanying symptoms at 0.5, 1, 2, 24, and 48 h postdose were analysed. In addition, the total cohort (full population, FP) was stratified into a prior nonresponder (PNR) group to observe the effectiveness and safety of rimegepant for relatively refractory migraine and a rimegepant and eptinezumab (RE) group to observe the effectiveness and safety of the combination of these drugs.
Results: By November 24th, 2023, 133 participants (FP, n = 133; PNR group, n = 40; RE group, n = 28) were enrolled, and 99 participants (FP, n = 99; PNR group, n = 30; RE group, n = 23) were included in the analysis. Rimegepant was effective in treating migraine in the FP and both subgroups, with a significant decreasing trend in the percentages of participants experiencing moderate to severe pain postdose (p < 0.05) and a marked increase in the percentages of participants who reported better/good outcomes in terms of pain intensity, functional ability, and accompanying symptoms at 0.5, 1, 2, 24, and 48 h postdose compared with predose. AEs were reported by 6% of participants in the FP, and all AEs were mild.
Conclusions: In the real world, rimegepant is effective in the acute treatment of migraine patients in China. The low incidence rate of AEs highlighted the favourable tolerability profile of rimegepant.
Trial registration: Clinicaltrials.gov NCT05709106. Retrospectively registered on 2023-02-01.
Keywords: Effectiveness; Migraine; Real-world; Rimegepant; Tolerability.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- (2018) Headache Classification Committee of the International Headache Society (IHS) The International Classification of Headache Disorders, 3rd edition. Cephalalgia 38:1–211 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials