AI-based fully automatic analysis of retinal vascular morphology in pediatric high myopia
- PMID: 39334037
- PMCID: PMC11437631
- DOI: 10.1186/s12886-024-03682-5
AI-based fully automatic analysis of retinal vascular morphology in pediatric high myopia
Abstract
Purpose: To investigate the changes in retinal vascular structures associated with various stages of myopia by designing automated software based on an artificial intelligence model.
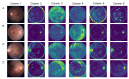
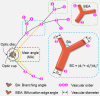
Methods: The study involved 1324 pediatric participants from the National Children's Medical Center in China, and 2366 high-quality retinal images and corresponding refractive parameters were obtained and analyzed. Spherical equivalent refraction (SER) degree was calculated. We proposed a data analysis model based on a combination of the Convolutional Neural Networks (CNN) model and the attention module to classify images, segment vascular structures, and measure vascular parameters, such as main angle (MA), branching angle (BA), bifurcation edge angle (BEA) and bifurcation edge coefficient (BEC). One-way ANOVA compared parameter measurements between the normal fundus, low myopia, moderate myopia, and high myopia groups.
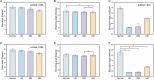
Results: The mean age was 9.85 ± 2.60 years, with an average SER of -1.49 ± 3.16D in the right eye and - 1.48 ± 3.13D in the left eye. There were 279 (12.38%) images in the normal group and 384 (16.23%) images in the high myopia group. Compared with normal fundus, the MA of fundus vessels in different myopic refractive groups was significantly reduced (P = 0.006, P = 0.004, P = 0.019, respectively), and the performance of the venous system was particularly obvious (P < 0.001). At the same time, the BEC decreased disproportionately (P < 0.001). Further analysis of fundus vascular parameters at different degrees of myopia showed that there were also significant differences in BA and branching coefficient (BC). The arterial BA value of the fundus vessel in the high myopia group was lower than that of other groups (P = 0.032, 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.22-4.86), while the venous BA values increased (P = 0.026). The BEC values of high myopia were higher than those of low and moderate myopia groups. When the loss function of our data classification model converged to 0.09, the model accuracy reached 94.19%.
Conclusion: The progression of myopia is associated with a series of quantitative retinal vascular parameters, particularly the vascular angles. As the degree of myopia increases, the diversity of vascular characteristics represented by these parameters also increases.
Keywords: Artificial intelligence; Automated analysis; High myopia; Retinal vessels.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Hernandez RJ, Roberts PA. El-Bouri advancing treatment of retinal disease through in silico trials. Progress Biomedical Eng. 2023;5:022002. - DOI
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

