COVID-19 risk factors and outcomes in individuals with stiff person syndrome spectrum disorders before and after omicron
- PMID: 39334235
- PMCID: PMC11428925
- DOI: 10.1186/s13023-024-03357-w
COVID-19 risk factors and outcomes in individuals with stiff person syndrome spectrum disorders before and after omicron
Abstract
Background: Stiff person syndrome spectrum disorders (SPSD) are rare, disabling disorders of the nervous system that are associated with risk factors for Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). However, limited data exist on the overall impact of COVID-19 on SPSD.
Methods: Patients with SPSD and COVID-19 who are followed at Johns Hopkins SPS Center were included. Demographics and SPSD characteristics along with COVID-19-specific data were recorded.
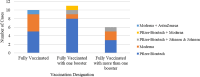
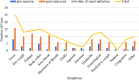
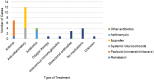
Results: Thirty-five cases of SPSD with COVID-19 cases were reported during the study time period. Mean age of the cohort was 56 (SD ± 10) and most were female (66.7%). Eighty percent of the COVID-19 cases were confirmed with testing, and the rest were highly suggestive of COVID-19. COVID-19 comorbidities among patients were hypertension (n = 6), diabetes (n = 6), obesity (n = 5), and cardiovascular disease (n = 4). The majority of participants were on immune therapies and/or benzodiazepines. Out of the cases reported, only 2 required hospitalization, both of whom had diabetes, and one was on immunosuppressive therapy. The majority of cases were post-full-vaccination cases. Fever was the most common COVID-19-associated symptom. Transient neurological symptoms were also reported.
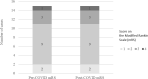
Conclusion: Risk factors for developing severe COVID-19 in SPSD appear to be the same as historical data in the general population. Importantly, COVID-19 did not appear to be associated with worsening SPSD post-COVID-19. Vaccination may have played a role in preventing severe cases of COVID-19.
Keywords: COVID-19; Neurology; SPSD; Stiff person syndrome; Vaccination.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

