Electroacupuncture inhibited carrageenan-induced pain aversion by activating GABAergic neurons in the ACC
- PMID: 39334299
- PMCID: PMC11428560
- DOI: 10.1186/s13041-024-01144-z
Electroacupuncture inhibited carrageenan-induced pain aversion by activating GABAergic neurons in the ACC
Abstract
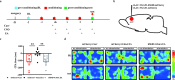
Pain aversion is an avoidance response to painful stimuli. Previous research has indicated that the anterior cingulate cortex (ACC) is involved in pain aversion processing. However, as interneurons, the role of GABAergic neurons in the ACC (GABAACC neurons) in pain aversion is still unclear. Electroacupuncture (EA) has been shown to ameliorate pain aversion, but the mechanism is not clarified. The present study provided evidence that inhibition of GABAACC neurons contributed to pain aversion. EA alleviated pain aversion by activating GABAACC neurons in an intensity-dependent manner. Specifically, 0.3 mA EA stimulation showed better effects on pain aversion than 0.1 mA stimulation, which could be reversed by chemical genetic inhibition of GABAACC neurons. These results provide a novel mechanism by which EA alleviates pain aversion by reversing GABAACC neurons.
Keywords: Anterior cingulate cortex; Electroacupuncture; GABAergic neurons; Pain; Pain aversion.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the study was conducted without any commercial or financial relationships that could be considered a potential conflict of interest.
Figures






References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

