Metformin use and preeclampsia risk in women with diabetes: a two-country cohort analysis
- PMID: 39334302
- PMCID: PMC11438264
- DOI: 10.1186/s12916-024-03628-0
Metformin use and preeclampsia risk in women with diabetes: a two-country cohort analysis
Abstract
Background: Metformin is a hypoglycaemic medication that has been proposed to treat or prevent preeclampsia. Combining national birth data from Scotland and Sweden, we investigated whether metformin used during pregnancy was associated with an altered risk of developing a hypertensive disorder of pregnancy.
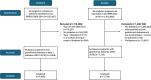
Methods: We utilised data from two population-based cohorts: Scotland (2012-2018) and Sweden (2007-2019). Nulliparous women with gestational diabetes or type 2 diabetes who had birth outcome data linked with medications prescribed during pregnancy were included. The association between metformin prescription and hypertensive disorders of pregnancy was characterised using inverse probability weighted regression analysis, adjusting for variables that predict metformin use and potential confounders. Adverse neonatal outcomes were included as secondary outcomes. Results from both countries were then combined in a meta-analysis using a random effects model.
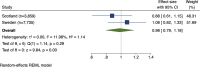
Results: The Scottish cohort included 3859 women with gestational diabetes or type 2 diabetes. Of these women, 30.8% (n = 1187) received at least one metformin prescription during pregnancy. For Sweden, 7771 women with gestational diabetes were included where 19.3% (1498) used metformin during pregnancy. Metformin prescription was not associated with an altered risk of any hypertensive disorder of pregnancy (Scotland adjusted relative risk (aRR) 0.88 [95% confidence interval (CI) 0.66-1.19]; Sweden aRR 1.08 [95% CI 0.86-1.37]) or preeclampsia (Scotland aRR 1.02 [95% CI 0.66-1.60]; Sweden aRR 1.00 [95% CI 0.72-1.39]). Combining adjusted results in a meta-analysis produced similar findings, with a pooled RR of 0.98 (95% CI 0.79-1.18) for any hypertensive disorder and RR 1.01 ([95% CI 0.73-1.28]) for preeclampsia. For neonatal outcomes, metformin was associated with a reduced risk of birthweight > 4500 g in Scotland (aRR 0.39 [95% CI 0.21-0.71]) but not in Sweden. There was no association between metformin and preterm birth or birthweight < 3rd or < 10th percentiles. Pooling results from both countries, metformin was not associated with adverse neonatal outcomes, including preterm birth (RR 1.00 [95% CI 0.89-1.13]), and birthweight < 10th percentile (RR 0.82 [95% CI 0.60-1.13]) or < 3rd percentile (RR 0.78 [95% CI 0.41-1.48]).
Conclusions: In this two-country analysis, metformin use in pregnancy among women with diabetes was not associated with an altered risk of developing any hypertensive disorder of pregnancy. In the combined meta-analysis, metformin was not associated with an altered risk of adverse neonatal outcomes.
Keywords: Gestational diabetes; Gestational hypertension; Metformin; Pre-eclampsia; Pregnancy; Pregnancy-induced hypertension.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Abalos E, Cuesta C, Grosso AL, Chou D, Say L. Global and regional estimates of preeclampsia and eclampsia: a systematic review. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol. 2013;170:1–7. - PubMed
-
- Rolnik DL, Wright D, Poon LCY, Syngelaki A, O’Gorman N, de Paco MC, et al. ASPRE trial: performance of screening for preterm pre-eclampsia. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol. 2017;50:492–5. - PubMed
-
- von Dadelszen P, Syngelaki A, Akolekar R, Magee LA, Nicolaides KH. Preterm and term pre-eclampsia: Relative burdens of maternal and perinatal complications. BJOG. 2023;130:524–30. - PubMed
-
- Brownfoot FC, Hastie R, Hannan NJ, Cannon P, Tuohey L, Parry LJ, et al. Metformin as a prevention and treatment for preeclampsia: effects on soluble fms-like tyrosine kinase 1 and soluble endoglin secretion and endothelial dysfunction. AJOG. 2016;214:356.e1-356.e15. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical