Effectiveness of DL-3-n-butylphthalide in the treatment of poststroke cognitive impairment and its associated predictive cytokines: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 39334406
- PMCID: PMC11430564
- DOI: 10.1186/s40360-024-00793-z
Effectiveness of DL-3-n-butylphthalide in the treatment of poststroke cognitive impairment and its associated predictive cytokines: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: The efficacy of DL-3-n-butylphthalide (NBP) in the treatment of post-stroke cognitive impairment (PSCI) has been reported previously. However, the course of treatment that shows curative effect and cytokines predictive of the efficacy of NBP in the treatment of PSCI have not been systematically evaluated. This study aimed to assess the efficacy, course of treatment, and cytokines that can predict the effectiveness of NBP in treating poststroke cognitive impairment PSCI.
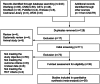
Methods: This study has been registered with PROSPERO (registration number CRD42024518768). Randomized controlled trial (RCT) data dated by November 12, 2023 were retrieved from the PubMed, Embase, Cochrane Library, Web of Science, Wanfang, CNKI, CSTJ, and SinoMed databases using medical subject terms combined with free words. The updated Cochrane RoB-I Risk of Bias tool was utilized for literature quality evaluation. Statistical analysis were carried out using Review Manager 5.4.1 software.
Results: Thirty-eight original studies involving 5417 PSCI patients were analyzed. The results showed that NBP had a beneficial impact on cognitive function in PSCI patients when used alone or in combination therapy, as assessed by the Mini-mental State Examination (MMSE) and Montreal Cognitive Assessment (MoCA) scale. The effect sizes were significant for both monotherapy and combination therapy. Subgroup analyses based on treatment cycle indicated that NBP enhanced cognitive function in PSCI patients from 1 week after intervention: MMSE (SMD = 0.43, 95% CI [0.28, 0.58], P < 0.001), MoCA (SMD = 0.44, 95% CI [0.27, 0.61], P < 0.001). There was a cumulative enhancement in cognitive function within 6 months after NBP treatment based on the MoCA scores (SMD = 0.61, 95% CI [0.30, 0.91], P < 0.001). Furthermore, decreased levels of the cytokines Hs-CRP, TNF-α, IL-6, IL-8, Hcy, NSE, MDA, MMP-9, and Cys-C (SMD = -2.28, 95% CI [-2.97, 1.58], P < 0.001) and increased levels of BDNF, VEGF, and TIMP-1 (SMD = 2.80, 95% CI [1.66, 3.94], P < 0.001) were also predictive of treatment efficacy.
Conclusion: NBP plays a beneficial role in improving cognitive function in PSCI patients, and their prognoses could be predicted by serum cytokine levels. However, high-quality, multicenter, multisample, and RCTs are still needed to confirm the clinical validity of NBP due to its low methodological quality.
Keywords: Cognitive function; MMSE; MoCA; Potential mechanisms; Randomized controlled trial.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Efficacy and Safety of DL-3-n-Butylphthalide in the Treatment of Poststroke Cognitive Impairment: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Jan 25;12:810297. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.810297. eCollection 2021. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35145408 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Efficacy of combination scalp acupuncture for post-stroke cognitive impairment: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Front Neurosci. 2024 Nov 29;18:1468331. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2024.1468331. eCollection 2024. Front Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 39678533 Free PMC article.
-
Systematic review and network meta-analysis of effects of noninvasive brain stimulation on post-stroke cognitive impairment.Front Neurosci. 2022 Dec 28;16:1082383. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2022.1082383. eCollection 2022. Front Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 36643019 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy and safety of acupuncture combined with rehabilitation training for poststroke cognitive impairment: A systematic review and meta-analysis.J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 2023 Sep;32(9):107231. doi: 10.1016/j.jstrokecerebrovasdis.2023.107231. Epub 2023 Jul 18. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 2023. PMID: 37473532
-
Protocol of End-PSCI trial: a multicenter, randomized controlled trial to evaluate the effects of DL-3-n-butylphthalide on delayed-onset post stroke cognitive impairment.BMC Neurol. 2022 Nov 16;22(1):435. doi: 10.1186/s12883-022-02957-y. BMC Neurol. 2022. PMID: 36384493 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wang K, Dong Q. Expert consensus on poststroke cognitive impairment management 2021. Chin J Stroke. 2021;16(4):376–389. 10.3969/j.issn.1673-5765.2021.04.011. [In Chinese].
-
- Ihle-Hansen H, Thommessen B, Wyller TB, Engedal K, Øksengård AR, Stenset V, et al. Incidence and subtypes of MCI and dementia 1 year after first-ever stroke in patients without pre-existing cognitive impairment. Dement Geriatr Cogn Disord. 2011;32(6):401–7. - PubMed
-
- Fride Y, Adamit T, Maeir A, Ben Assayag E, Bornstein NM, Korczyn AD, et al. What are the correlates of cognition and participation to return to work after first ever mild stroke? Top Stroke Rehabil. 2015;22(5):317–25. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- tsqn202312392/Taishan Scholar Project of Shandong Province
- LKJGG2021W126/Science and Technology Development Plan Project of Shandong Geriatrics Society
- RZ2300002690/Outstanding Young Talents Project in Health of Qilu and the youth talent training program from Qingdao medical college of Qingdao University
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

