Single-cell sequencing to multi-omics: technologies and applications
- PMID: 39334490
- PMCID: PMC11438019
- DOI: 10.1186/s40364-024-00643-4
Single-cell sequencing to multi-omics: technologies and applications
Abstract
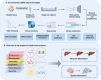
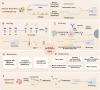
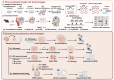
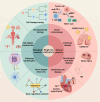
Cells, as the fundamental units of life, contain multidimensional spatiotemporal information. Single-cell RNA sequencing (scRNA-seq) is revolutionizing biomedical science by analyzing cellular state and intercellular heterogeneity. Undoubtedly, single-cell transcriptomics has emerged as one of the most vibrant research fields today. With the optimization and innovation of single-cell sequencing technologies, the intricate multidimensional details concealed within cells are gradually unveiled. The combination of scRNA-seq and other multi-omics is at the forefront of the single-cell field. This involves simultaneously measuring various omics data within individual cells, expanding our understanding across a broader spectrum of dimensions. Single-cell multi-omics precisely captures the multidimensional aspects of single-cell transcriptomes, immune repertoire, spatial information, temporal information, epitopes, and other omics in diverse spatiotemporal contexts. In addition to depicting the cell atlas of normal or diseased tissues, it also provides a cornerstone for studying cell differentiation and development patterns, disease heterogeneity, drug resistance mechanisms, and treatment strategies. Herein, we review traditional single-cell sequencing technologies and outline the latest advancements in single-cell multi-omics. We summarize the current status and challenges of applying single-cell multi-omics technologies to biological research and clinical applications. Finally, we discuss the limitations and challenges of single-cell multi-omics and potential strategies to address them.
Keywords: Computational biology; Metabolome; Microbiome; Proteomics; Single-cell multi-omics; Spatial transcriptomics; scBCR-seq; scRNA-seq; scTCR-seq.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

