Risk Factors and 20-Year Time-Trend in Childhood Overweight and Obesity in Switzerland: A Repeated Cross-Sectional Study
- PMID: 39334583
- PMCID: PMC11430791
- DOI: 10.3390/children11091050
Risk Factors and 20-Year Time-Trend in Childhood Overweight and Obesity in Switzerland: A Repeated Cross-Sectional Study
Abstract
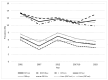
Background/Objective: Even though global childhood obesity rates keep increasing, stabilization has been shown over the past decade in several countries, including Switzerland. We aimed to investigate the trends in childhood overweight and obesity over the past 21 years in Switzerland and to identify the associated risk factors. Methods: Using cluster sampling, we recruited a national sample of 6-12-year-old children in Switzerland (n = 1245). We conducted anthropometric measurements and assessed risk factors using a self-administered questionnaire. We investigated the time trend by including data from four comparable previous surveys conducted since 2002. Results: We found a prevalence of overweight, including obesity, of 16.1 (14.1-18.2)%, with a significantly higher proportion in boys (18.6 (15.5-21.6)%) compared to girls (13.7 (11.0-16.4)%). We found a small but significant reduction in the prevalence of overweight including obesity over time (p = 0.005), but not of obesity alone (p = 0.099). The most important risk factors for obesity were parental education, parental origin, media consumption, as well as several dietary factors. Conclusions: Despite a slight decreasing trend in childhood overweight in Switzerland, it remains a public health concern. Prevention programs should focus on migrant families and those with low education and emphasize the risks of sedentary behavior and the importance of a healthy diet.
Keywords: Switzerland; children; diet; media consumption; obesity; overweight; parental factors; physical activity; risk factors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. Representatives of the Swiss Federal Office of Public Health, who funded this study, were involved in the selection of questions included in the questionnaire distributed to the children. They were not involved in any other aspects of the study.
Figures
References
-
- Roth G.A., Mensah G.A., Johnson C.O., Addolorato G., Ammirati E., Baddour L.M., Barengo N.C., Beaton A.Z., Benjamin E.J., Benziger C.P., et al. Global Burden of Cardiovascular Diseases and Risk Factors, 1990–2019 Update From the GBD 2019 Study. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2020;76:2982–3021. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2020.11.010. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous