Challenges in Pediatric Liver Retransplantation: A Technical Perspective
- PMID: 39334612
- PMCID: PMC11430149
- DOI: 10.3390/children11091079
Challenges in Pediatric Liver Retransplantation: A Technical Perspective
Abstract
Background/objectives: Liver retransplantation (reLT) is the only option for pediatric patients experiencing graft loss. Despite recent advancements in surgical techniques and perioperative management, it remains a high-risk procedure. Our aim is to describe our experience in pediatric reLT, focusing on the technical aspects and surgical challenges.
Methods: We systematically analyzed surgical reports from pediatric reLT performed at our center between 2006 and 2023 to identify recurrent intraoperative findings and specific surgical techniques. We focused on challenges encountered during different phases of reLT, including hepatectomy, vascular, and biliary reconstruction. Additionally, we compared patient and graft survival rates among different groups.
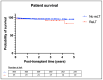
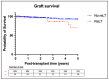
Results: During the study period, 23 children underwent 25 reLT procedures at our center. Major surgical challenges included complex hepatectomy and vascular reconstructions, necessitating tailored approaches. Our analysis shows that patient and graft survival were significantly lower for reLT compared to primary transplantation (p = 0.002). Early reLT had a significantly lower graft survival compared to late reLT (p = 0.002), although patient survival was comparable (p = 0.278). Patient and graft survival rates were comparable between the first and second reLT (p = 0.300, p = 0.597). Patient survival tended to be higher after living-donor liver transplantation (LDLT) compared to deceased-donor liver transplantation (DDLT), although the difference was not statistically significant (p = 0.511).
Conclusions: Pediatric reLT involves significant technical challenges and lower survival rates. Advances in perioperative management are crucial for improving outcomes. Further research is needed to optimize surgical strategies and evaluate the long-term benefits of LDLT in pediatric reLT.
Keywords: living-donor liver transplantation; pediatric liver transplantation; retransplantation; surgical technique.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources