Influences of Maternal Nutrition and Lifestyle Factors on Early Childhood Oral Health: A Systematic Review of Mechanisms and Intervention Strategies
- PMID: 39334639
- PMCID: PMC11430575
- DOI: 10.3390/children11091107
Influences of Maternal Nutrition and Lifestyle Factors on Early Childhood Oral Health: A Systematic Review of Mechanisms and Intervention Strategies
Abstract
Background: This systematic review and meta-analysis examined the impact of maternal nutrition and lifestyle factors on early childhood oral health. The review focused on the effects of maternal vitamin D levels and smoking during pregnancy on children's dental health outcomes.
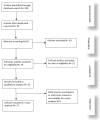
Methods: A comprehensive literature search was conducted across PubMed, Scopus, and Web of Science, yielding 23 that were included for analysis. The quality of the studies was assessed using the Newcastle-Ottawa Scale. The effect estimates were pooled through a random effect model. All analyses were carried out using the R program.
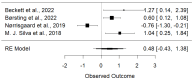
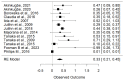
Results: Most studies in our systematic review showed a significant association between maternal vitamin D and smoking during pregnancy and childhood dental health outcomes. Meta-analysis revealed a significant association between maternal vitamin D levels and children's dental health (OR = 1.30, 95% CI: 0.49 to 3.45, p < 0.001). Maternal smoking during pregnancy was strongly linked to an increased risk of childhood dental caries (OR = 0.3290, 95% CI: 0.2089-0.4491, p < 0.0001).
Conclusions: These findings underscore the crucial role of maternal health behaviors in shaping children's oral health trajectories. This study emphasizes the need for integrated public health interventions promoting healthier maternal behaviors and early preventive dental care.
Keywords: dental caries prevention; early childhood oral health; maternal nutrition; maternal smoking; vitamin D.
Conflict of interest statement
The author confirms that this research was carried out without any commercial or financial relationships that might be perceived as potential conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

