Comparison between Liquid and Tablet Formulations in the Treatment of Congenital Hypothyroidism up to 3 Years of Age: The First Italian Study
- PMID: 39334669
- PMCID: PMC11430788
- DOI: 10.3390/children11091136
Comparison between Liquid and Tablet Formulations in the Treatment of Congenital Hypothyroidism up to 3 Years of Age: The First Italian Study
Abstract
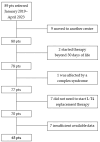
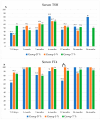
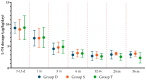
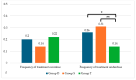
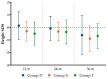
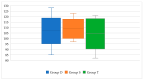
Background/Objectives: Levothyroxine (L-T4) is available for use in congenital hypothyroidism (CH) in three formulations: tablets, drops, and oral solution. This study aims to compare the efficacy and safety of all three L-T4 formulations. Methods: We enrolled 63 children born between January 2019 and April 2023 in the Emilia-Romagna Region (Italy) and diagnosed with CH by newborn screening. They were divided according to the L-T4 formulation used: drops (Group D), oral solution (Group S), and tablets (Group T). Clinical and laboratory data were collected up to 3 years after the start of replacement therapy. Results: Serum-free thyroxine (sFT4) and thyroid stimulating hormone (sTSH) normalization occurred within the first month of treatment in most patients of all groups. No negative effects on growth and cognitive development were observed. At 7-15 days we found higher median sTSH levels (p = 0.031) and a greater percentage of patients with sTSH > 5 µU/mL (p = 0.011) in Group S than in Group T, but comparable sFT4 levels. At 12 months, a greater percentage of patients of Group D showed sFT4 values below the normal range than Group S (p = 0.011) and Group T (p = 0.038); Conclusions: Overall, our study reported an equal efficacy of the L-T4 oral solution compared to drops and tablets in CH treatment. A larger series of patients and a long-term follow-up are needed.
Keywords: congenital hypothyroidism; levothyroxine efficacy; levothyroxine formulation; levothyroxine liquid formulation; neurodevelopmental outcome; newborn screening.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Van Trotsenburg P., Stoupa A., Léger J., Rohrer T., Peters C., Fugazzola L., Cassio A., Heinrichs C., Beauloye V., Pohlenz J., et al. Congenital Hypothyroidism: A 2020–2021 Consensus Guidelines Update—An ENDO-European Reference Network Initiative Endorsed by the European Society for Pediatric Endocrinology and the European Society for Endocrinology. Thyroid. 2021;31:387–419. doi: 10.1089/thy.2020.0333. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Olivieri A., Corbetta C., Weber G., Vigone M.C., Fazzini C., Medda E. The Italian Study Group for Congenital Hypothyroidism Congenital Hypothyroidism Due to Defects of Thyroid Development and Mild Increase of TSH at Screening: Data From the Italian National Registry of Infants With Congenital Hypothyroidism. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2013;98:1403–1408. doi: 10.1210/jc.2012-3273. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Stagi S., Municchi G., Ferrari M., Wasniewska M.G. An Overview on Different L-Thyroxine (l-T4) Formulations and Factors Potentially Influencing the Treatment of Congenital Hypothyroidism During the First 3 Years of Life. Front. Endocrinol. 2022;13:859487. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2022.859487. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Cassio A., Monti S., Rizzello A., Bettocchi I., Baronio F., D’Addabbo G., Bal M.O., Balsamo A. Comparison between Liquid and Tablet Formulations of Levothyroxine in the Initial Treatment of Congenital Hypothyroidism. J. Pediatr. 2013;162:1264–1269.e2. doi: 10.1016/j.jpeds.2012.11.070. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

