Determination of Biologically Active Compounds and Antioxidant Capacity In Vitro in Fruit of Small Cranberries (Vaccinium oxycoccos L.) Growing in Natural Habitats in Lithuania
- PMID: 39334704
- PMCID: PMC11428458
- DOI: 10.3390/antiox13091045
Determination of Biologically Active Compounds and Antioxidant Capacity In Vitro in Fruit of Small Cranberries (Vaccinium oxycoccos L.) Growing in Natural Habitats in Lithuania
Abstract
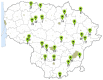
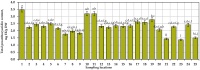
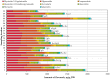
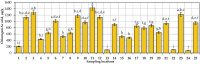
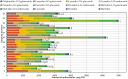
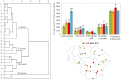
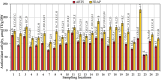
The composition of flavonols, proanthocyanidins, anthocyanins, triterpene compounds, and chlorogenic acid in small cranberry fruit samples collected in natural habitats in Lithuania and variation in the antioxidant capacity of cranberry fruit extracts was determined. This study showed that in the flavonol group, hyperoside and myricetin-3-O-galactoside predominated in cranberry fruit samples; in the anthocyanin group, the predominant compounds were cyanidin-3-O-galactoside, cyanidin-3-O-arabinoside, peonidin-3-O-galactoside, and peonidin-3-O-arabinoside, and in the group of triterpene compounds, ursolic acid was predominant. The highest total amounts of flavonols and anthocyanins were found in the samples collected in Čepkeliai State Strict Nature Reserve (2079.44 ± 102.99 μg/g and 6993.79 ± 350.22 μg/g, respectively). Cluster analysis of the chemical composition of small cranberry fruit samples revealed trends in the accumulation of bioactive compounds in cranberry fruit. Cranberry fruit samples collected in central Lithuania had higher levels of triterpene compounds. Statistical correlation analysis showed the strongest correlation between the quantitative composition of cyanidin-3-O-arabinoside and peonidin-3-O-arabinoside and the reducing capacity of the ethanolic extracts of the cranberry fruit samples assessed in vitro by the FRAP assay (r = 0.882, p < 0.01 and r = 0.805, p < 0.01, respectively). Summarizing the results, the geographical factor affects the variation of the quantitative composition of biologically active compounds in cranberry fruit samples.
Keywords: Vaccinium oxycoccos; anthocyanins; antioxidant capacity in vitro; chlorogenic acid; flavonols; natural habitats; proanthocyanidins; triterpene compounds.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Rodriguez-Bonilla L., Rohde J., Matusinec D., Zalapa J. Cross-transferability analysis of SSR markers developed from the American cranberry (Vaccinium macrocarpon Ait.) to other Vaccinium species of agricultural importance. Genet. Resour. Crop Evol. 2019;66:1713–1725. doi: 10.1007/s10722-019-00826-1. - DOI
-
- Shotyk W., Bicalho B., Grant-Weaver I., Stachiw S. A geochemical perspective on the natural abundance and predominant sources of trace elements in cranberries (Vaccinium oxycoccus) from remote bogs in the boreal region of Northern Alberta, Canada. Sci. Total Environ. 2019;650:1652–1663. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.06.248. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Česonienė L., Daubaras R., Paulauskas A., Žukauskienė J., Zych M. Morphological and genetic diversity of European Cranberry (Vaccinium oxycoccos L., Ericaceae) clones in Lithuanian reserves. Acta Soc. Bot. Pol. 2013;82:211–217. doi: 10.5586/asbp.2013.026. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

