Multi-Omics Exploration of the Mechanism of Curcumol to Reduce Invasion and Metastasis of Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma by Inhibiting NCL/EBNA1-Mediated UBE2C Upregulation
- PMID: 39334908
- PMCID: PMC11430640
- DOI: 10.3390/biom14091142
Multi-Omics Exploration of the Mechanism of Curcumol to Reduce Invasion and Metastasis of Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma by Inhibiting NCL/EBNA1-Mediated UBE2C Upregulation
Abstract
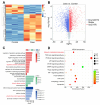
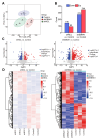
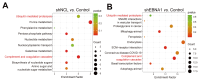
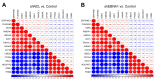
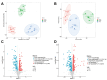
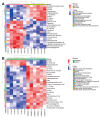
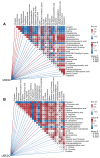
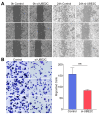
Nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC) is closely linked to Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) infection. Curcumae Rhizoma, a traditional Chinese herb, has shown antitumor effects, primarily through its component curcumol (Cur), which has been shown to reduce NPC cell invasion and migration by targeting nucleolin (NCL) and Epstein-Barr Virus Nuclear Antigen 1 (EBNA1). We constructed an EBV-positive NPC cell model using C666-1 cells and performed transcriptomics studies after treatment with curcumol, which revealed a significant enrichment of ubiquitin-mediated proteolysis, the PI3K-AKT and mTOR signaling pathways, cell cycle and apoptosis involved in tumor invasion and migration. To investigate the importance of NCL and EBNA1 in curcumol-resistant EBV-positive NPC, we performed a multi-omics study using short hairpin NCL (shNCL) and shEBNA1 EBV-positive NPC cells, and the proteomics results showed enrichment in complement and coagulation cascades and ubiquitin-mediated proteolysis signaling pathways. Here, we focused on ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme E2C (UBE2C), which plays an important role in the ubiquitin-mediated proteolysis signaling pathway. In addition, metabolomics revealed that UBE2C is highly associated with 4-Aminobutanoic acid (GABA). In vitro studies further validated the function of the key targets, suggesting that UBE2C plays an important role in NCL and EBNA1-mediated curcumol resistance to nasopharyngeal carcinoma invasion and metastasis.
Keywords: EBNA1; NCL; UBE2C; curcumol; metabolomics; nasopharyngeal carcinoma; proteomics; transcriptomics.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

