Murepavadin Enhances the Killing Efficacy of Ciprofloxacin against Pseudomonas aeruginosa by Inhibiting Drug Efflux
- PMID: 39334985
- PMCID: PMC11429200
- DOI: 10.3390/antibiotics13090810
Murepavadin Enhances the Killing Efficacy of Ciprofloxacin against Pseudomonas aeruginosa by Inhibiting Drug Efflux
Abstract
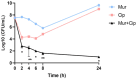
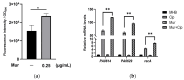
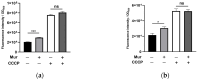
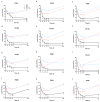
Pseudomonas aeruginosa is a multidrug-resistant Gram-negative pathogen and one of the leading causes of ventilator-associated pneumonia and infections in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and cystic fibrosis. Murepavadin is a peptidomimetic that specifically targets outer-membrane lipopolysaccharide transport protein LptD of P. aeruginosa. In this study, we find that murepavadin enhances the bactericidal efficacy of ciprofloxacin. We further demonstrate that murepavadin increases intracellular accumulation of ciprofloxacin by suppressing drug efflux. In addition, the murepavadin-ciprofloxacin combination exhibits a synergistic bactericidal effect in an acute murine pneumonia model. In conclusion, our results identify an effective drug combination for the treatment of P. aeruginosa infections.
Keywords: Pseudomonas aeruginosa; ciprofloxacin; murepavadin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures

References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

