Insights into the Virulence and Antimicrobial Resistance of Staphylococcus hyicus Isolates from Spanish Swine Farms
- PMID: 39335044
- PMCID: PMC11428503
- DOI: 10.3390/antibiotics13090871
Insights into the Virulence and Antimicrobial Resistance of Staphylococcus hyicus Isolates from Spanish Swine Farms
Abstract
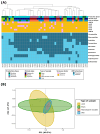
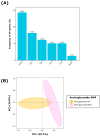
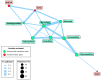
Staphylococcus hyicus is a significant pathogen in swine, primarily causing exudative epidermitis. Addressing S. hyicus infections requires both the characterization of virulence and antimicrobial resistance (AMR) in farm-recovered isolates. This study aimed to characterize the virulence, AMR, and biofilm formation of S. hyicus isolates from Spanish swine farms. A total of 49 isolates were analyzed, originating from animals with cutaneous, reproductive, and systemic clinical signs. Half of the isolates (49.0%) were positive for at least one virulence factor (VF) gene, with SHETA being the most frequent (28.6%). A high frequency of multidrug resistant (MDR) isolates was observed (83.7%), with significant resistance to commonly used antimicrobials, including lincosamides (83.7%), pleuromutilins (81.6%), penicillins (75.5%), and tetracyclines (73.5%). All isolates exhibited robust in vitro biofilm formation capacity (DC = 15.6 ± 7.0). Significant associations were found between VFs, biofilm formation, and AMR patterns, highlighting the link between the resistance to lincosamides and pleuromutilins (p < 0.001; Φ = 0.57) and macrolides (p < 0.001; Φ = 0.48), and the association of AMR with the ExhC and ExhD VF genes. These findings underscore the need for targeted diagnostics to improve management and therapeutic strategies to mitigate the impact of S. hyicus on swine production.
Keywords: Staphylococcus hyicus; antimicrobial resistance; biofilm formation; exfoliative toxins; exudative epidermitis; virulence.
Conflict of interest statement
Author Álvaro Aguarón-Turrientes was employed by the company Laboratorios SYVA. The remaining authors declare that this research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Characterization and antimicrobial resistance of Staphylococcus hyicus from swine exudative epidermitis in South Korea.BMC Vet Res. 2024 Nov 28;20(1):533. doi: 10.1186/s12917-024-04396-y. BMC Vet Res. 2024. PMID: 39609838 Free PMC article.
-
Multidrug resistant staphylococci isolated from pigs with exudative epidermitis in North eastern Region of India.Lett Appl Microbiol. 2021 May;72(5):535-541. doi: 10.1111/lam.13448. Epub 2021 Jan 25. Lett Appl Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 33421175
-
Antimicrobial Resistance Profile of Staphylococcus hyicus Strains Isolated from Brazilian Swine Herds.Antibiotics (Basel). 2022 Feb 6;11(2):205. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics11020205. Antibiotics (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35203808 Free PMC article.
-
Distribution of the putative virulence factor encoding gene sheta in Staphylococcus hyicus strains of various origins.J Vet Sci. 2008 Sep;9(3):327-9. doi: 10.4142/jvs.2008.9.3.327. J Vet Sci. 2008. PMID: 18716454 Free PMC article.
-
[Staphylococcus hyicus, the cause of exudative epidermitis of swine. Review].Berl Munch Tierarztl Wochenschr. 1990 Feb 1;103(2):60-3. Berl Munch Tierarztl Wochenschr. 1990. PMID: 2407232 Review. German.
References
-
- Wegener H.C., Skov-Jensen E.W. Exudative epidermitis. In: Straw B.E., Zimmerman J.J., D’Allaire S., Taylor D.J., editors. Diseases of Swine. 9th ed. Blackwell Pub; Ames, IA, USA: 2006. pp. 675–679.
-
- de Winter P.J.J., Verdonck M., de Kruif A., Devriese L.A., Haesebrouck F. Bacterial Endometritis and Vaginal Discharge in the Sow: Prevalence of Different Bacterial Species and Experimental Reproduction of the Syndrome. Anim. Reprod. Sci. 1995;37:325–335. doi: 10.1016/0378-4320(94)01342-J. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

